It starts with a simple ticket: “Login issue: user can’t access dashboard.”
By the time it’s escalated, reassigned, tagged, commented on, routed to engineering, then back to support…
That “simple” ticket has now passed through four tools, five people, and zero resolutions.
You’ve got Zendesk, which is built for support teams and Jira Service Management for technical teams.
But when your workflows span both, you’re caught between two platforms speaking two different languages—and your customers are stuck in the middle, waiting for a translator.
- On one side, Zendesk gives you polished workflows and great macros.
- But becomes a maze when you try to adapt it for internal operations or dev-heavy requests.
- On the other, Jira SM handles internal processes like a pro.
- But makes actual customer support feel like submitting a bug report to IT.
So the real question isn’t just “Which one is better?”
It’s: Why do you need multiple tools just to get one ticket resolved?
In this guide, we’ll break down where Zendesk and Jira SM shine, where they struggle, and what a better support experience looks like. One that works for your team and your customers.
Let’s get into it.
Zendesk vs Jira Service Management: General Overview
Zendesk Overview
Zendesk is a cloud-based customer service platform designed to help businesses deliver seamless support experiences across channels (email, chat, phone, or social).
It functions as an integrated customer support suite that combines self-service, live chat, messaging, voice support, and customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities into a single solution.
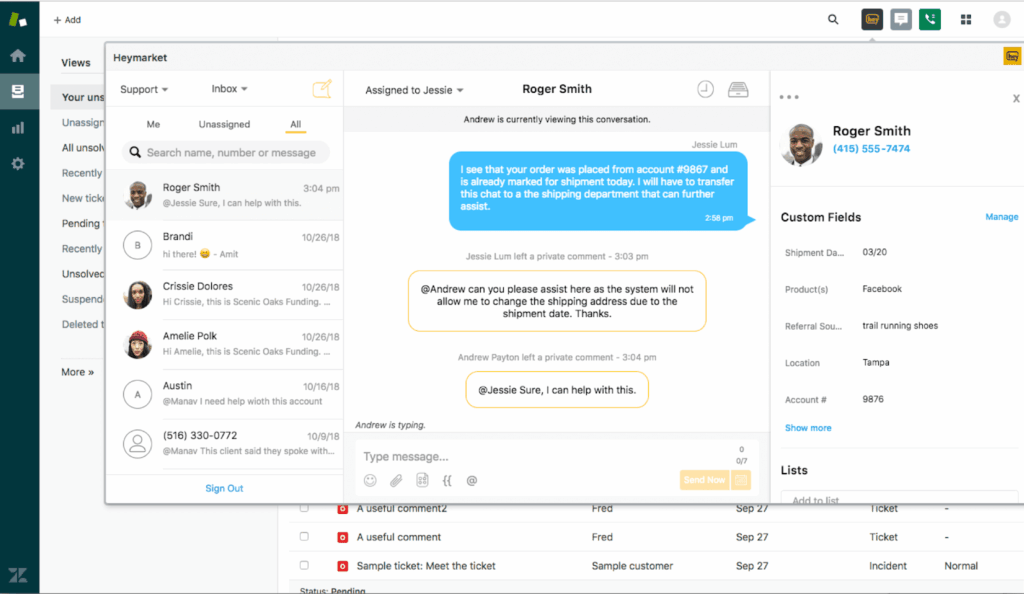
Zendesk’s support framework is built on a ‘ticketing-based’ workflow where all customer interactions via different channels are converted into a structured, trackable ticket.
- Tickets can be automatically routed using Triggers, Macros, and Automations.
- Agents can add tags, assign priority, set statuses, and define SLA timelines.
- Internal collaboration is supported with private notes and Light Agents (these non-support staff who can view and comment).
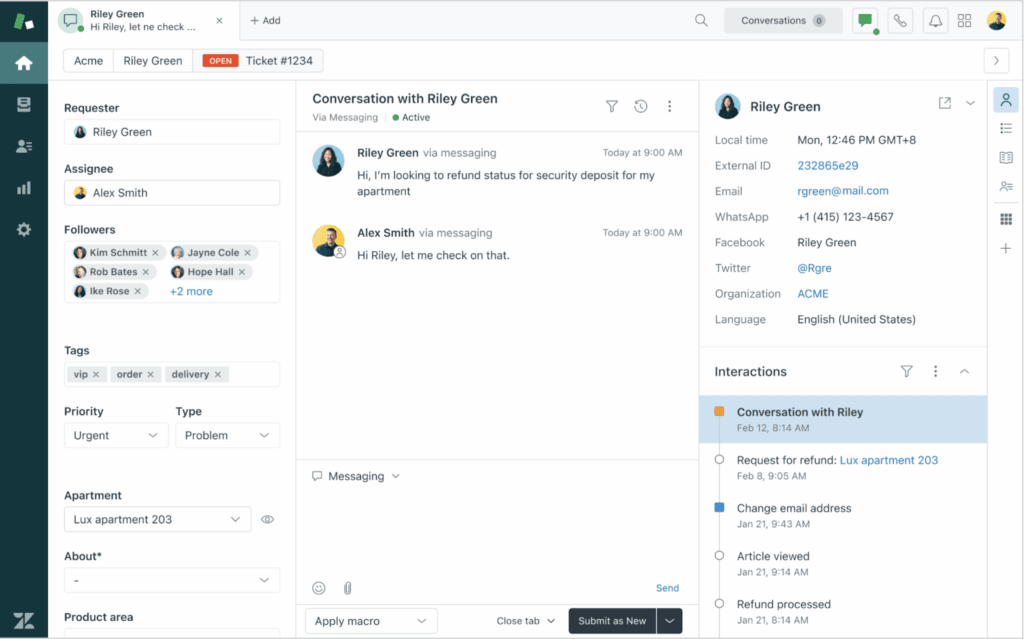
To streamline the entire interaction, agents can also leverage the ‘Agent Workspace’ feature to respond with prebuilt macros, escalate with internal notes, and use AI-suggested replies.
They can also pull in historical context, and collaborate with teammates without leaving the thread.
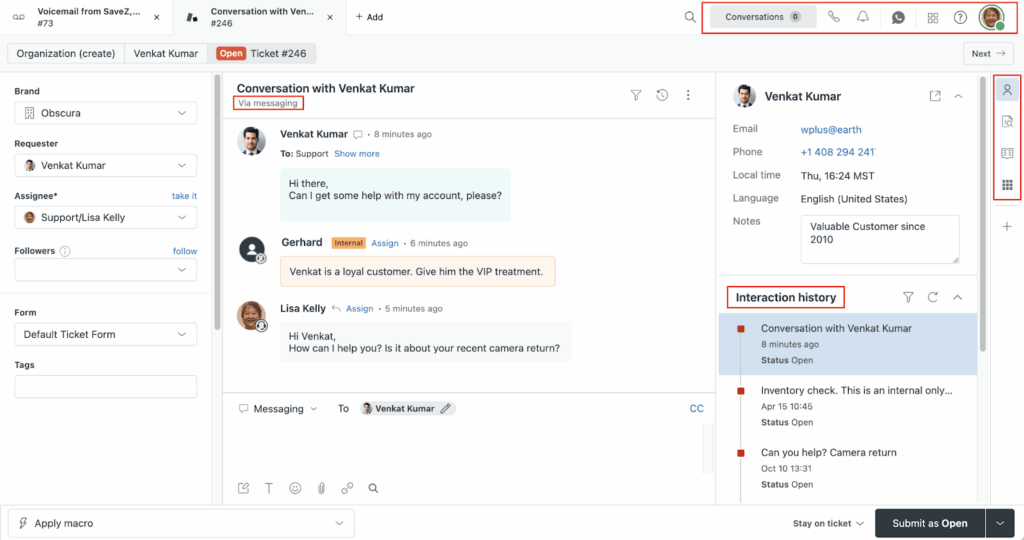
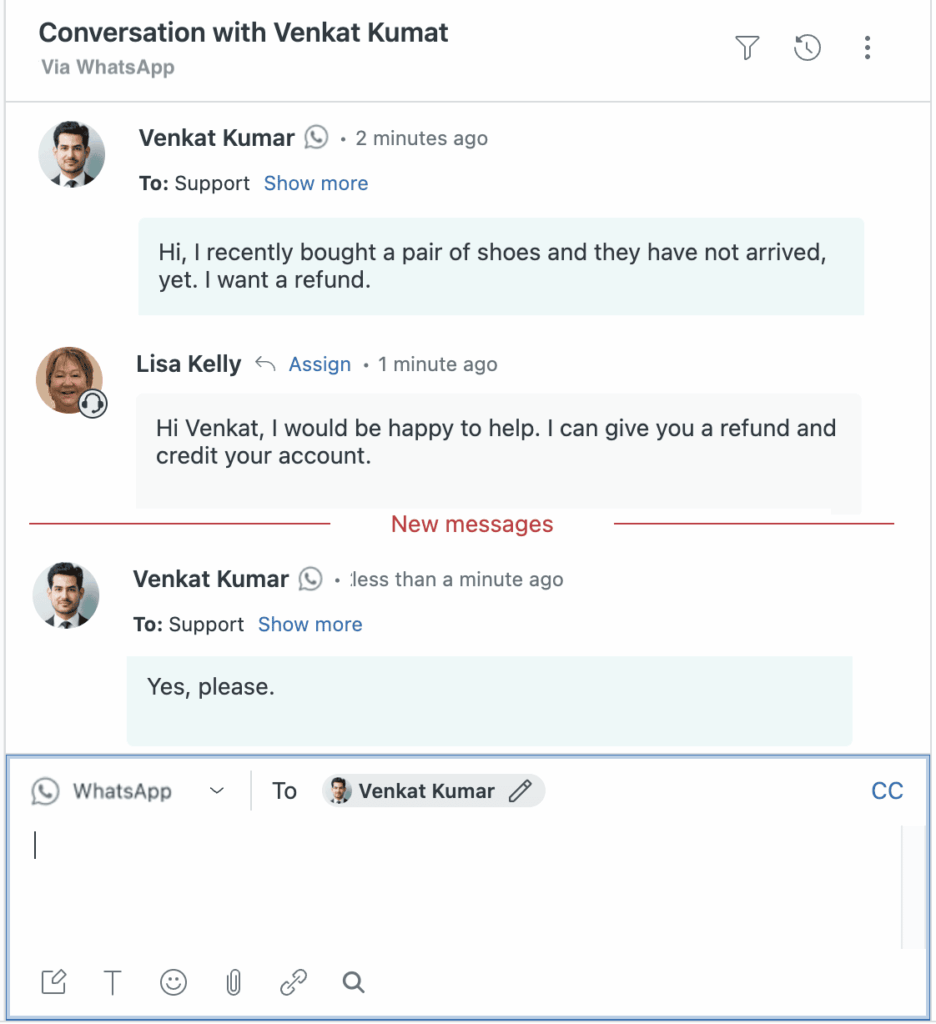
Another complicated but interesting aspect of Zendesk is its ecosystem.
You see, Zendesk offers different products that work together, giving you the flexibility of ‘cherry-picking’ your preferred support mix.
You’ve got:
- Zendesk Support. Core ticketing, macros, SLAs, triggers
- Zendesk Guide. Knowledge base and self-service portals
- Zendesk Talk: Call center solution for inbound and outbound voice support
- Zendesk Messaging. Real-time, asynchronous communication tools
- Zendesk Explore. Advanced analytics and reporting dashboards
- Zendesk Sunshine: A flexible CRM framework for custom objects and customer data extensions
In addition, Zendesk features a robust marketplace of over 1,700+ third-party integration options with apps like Salesforce, HubSpot, Slack, Make, Zapier and several other solutions.
💡IN SHORT: Zendesk is powerful and built for structure, which is both its strength and limitation. If you need rigid control, enterprise-level permissions, and layered escalation rules, Zendesk can handle it. However, remember that set-up is rarely plug-and-play, automation logic can become dense, and cross-team collaboration often happens in silos.
Jira Service Management Overview
Jira Service Management (JSM) is Atlassian’s service desk solution, built on top of the popular Jira’s issue-tracking engine. It’s an internal helpdesk tool for technical teams such as IT, DevOps, and engineering.
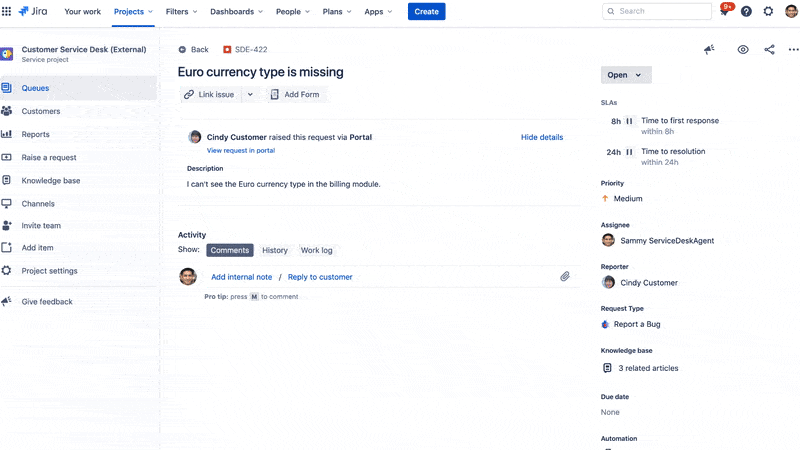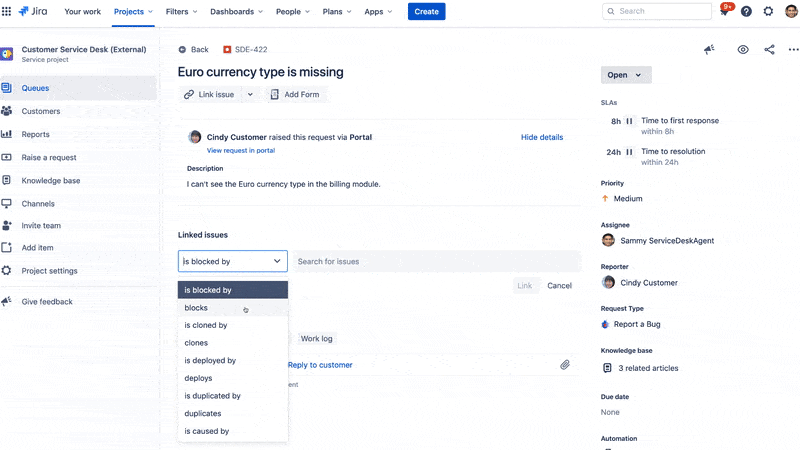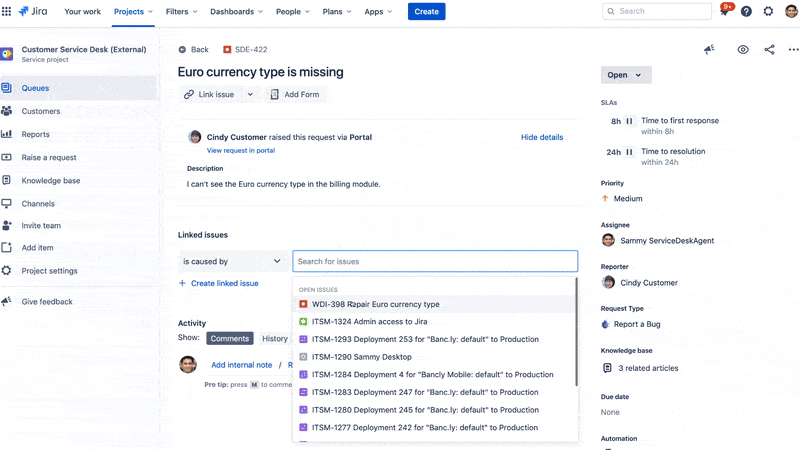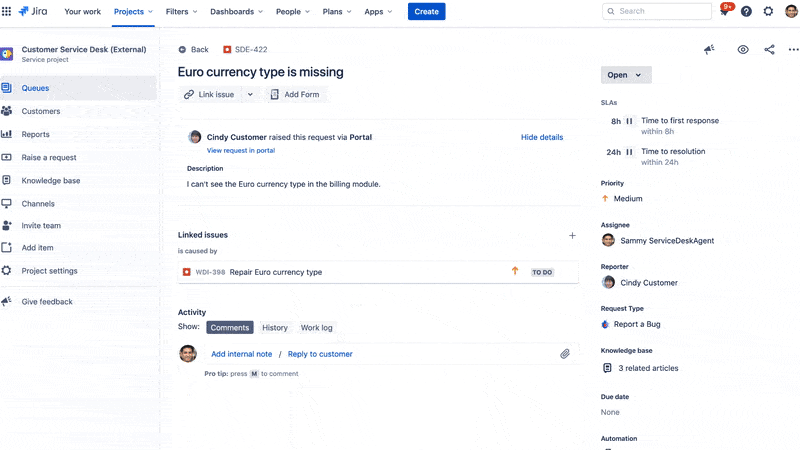
The platform helps teams manage incoming requests, incidents, problems, and changes in a structured, auditable way. Requests submitted via portals, emails, or chat are converted into Jira issues, allowing teams to route, prioritize, and track them using customizable workflows and SLAs.
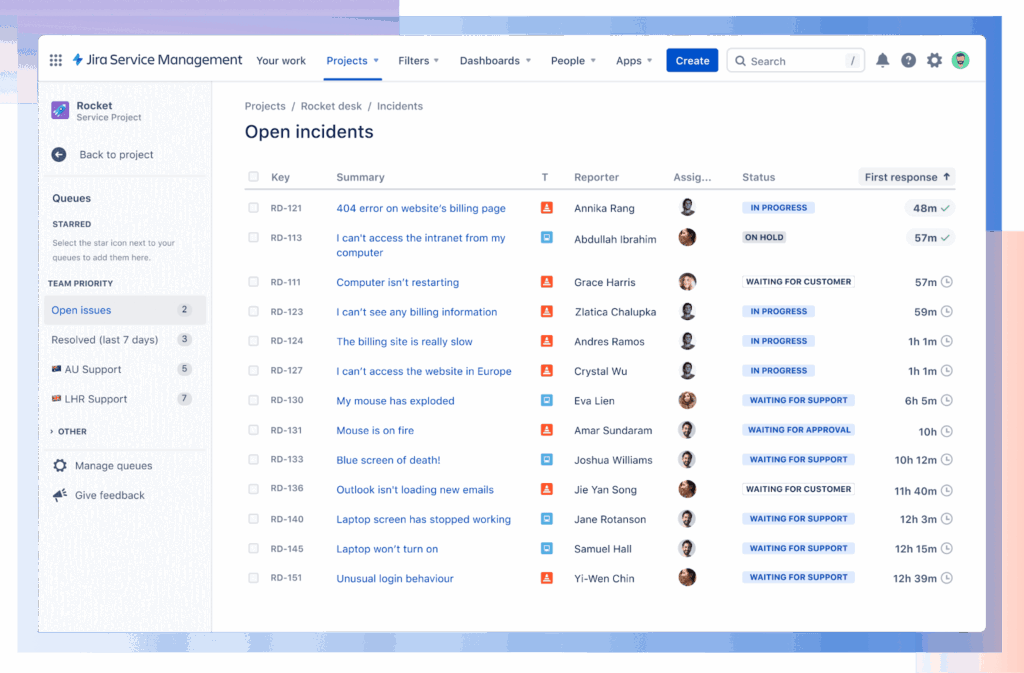
For example, users can create customizable self-service portals where employees or customers can raise tickets for support.
- Portals can be customized per team (e.g., IT, HR, Finance).
- Request types are mapped to backend issue types and workflows.
- Smart forms and conditional logic ensure relevant data is captured from users.
The portal also integrates with Confluence to suggest relevant knowledge base articles before a user submits a request.
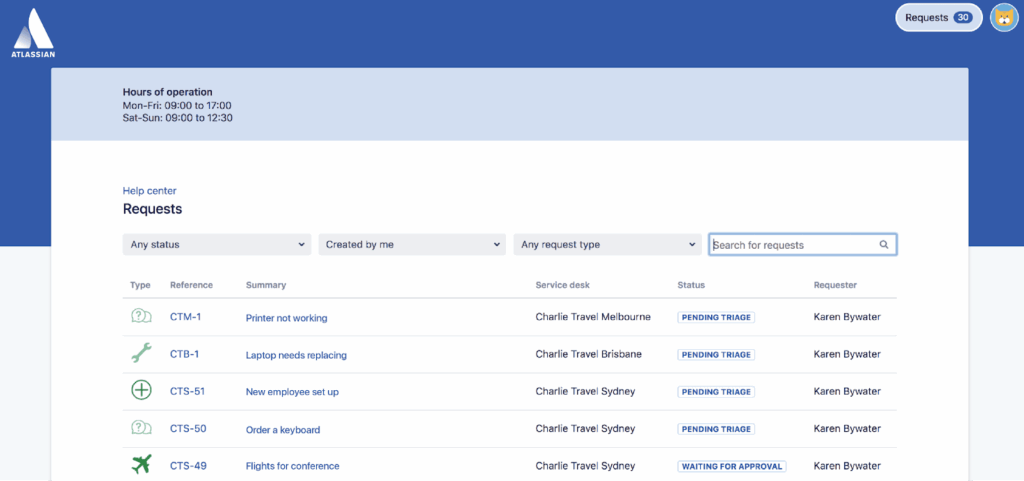
In addition, Jira Service Management offers seamless integration with other Atlassian products such as Jira Software, Bitbucket, and Opsgenie.
This means developers and service agents can work in the same environment without switching tools, making it easier to share tickets, link issues, escalate bugs, and document resolutions.
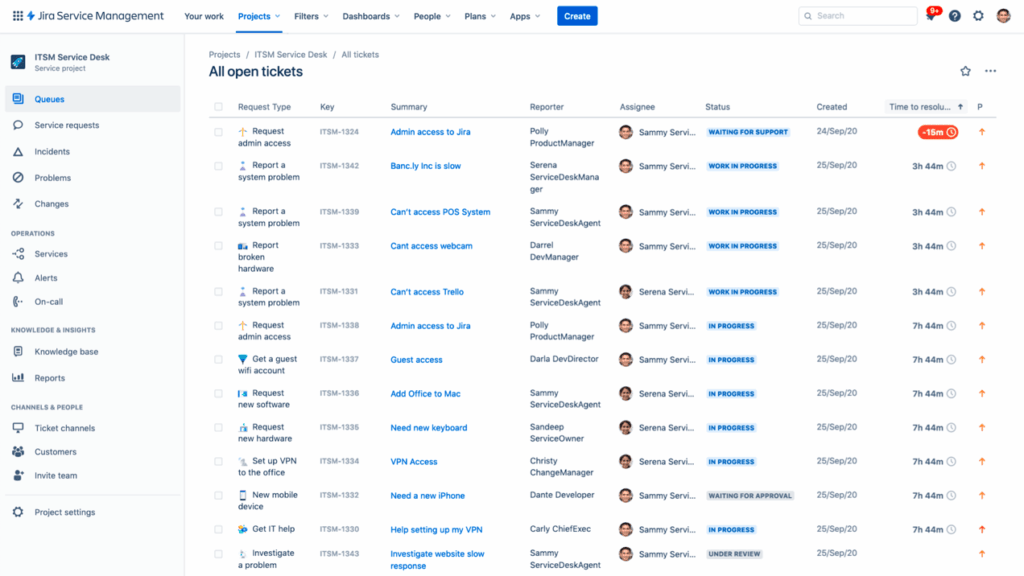
Other advanced features under the JSM umbrella include:
- Asset Management (via Assets, formerly Insight) to track hardware, software, and infrastructure
- Incident Management powered by integrations with Opsgenie for real-time alerting and on-call coordination
- Change Management with risk assessments, peer reviews, and automated approvals
💡IN SHORT: JSM is best for technical teams who want a tight feedback loop between users and builders. It bridges the gap between incidents in the field and tickets in a product backlog.
However, its interface is heavily Jira-centric, and for non-technical users or customer-facing agents, the learning curve can be steep.
Zendesk vs. Jira Service Management: Key Differences
Customer Support vs. ITSM
- Zendesk is fundamentally a customer service tool. Its interface, workflows, and key features are optimized for customer-facing agents who need to manage conversations, support tickets, and relationships across channels like email, chat, voice, and social media.
- Jira Service Management, on the other hand, was built from the ground up for IT and engineering teams. It follows strict ITIL principles and shines in areas like incident management, problem tracking, and change control.
🎯If your team is managing external customers across multiple touchpoints, Zendesk’s CX-first design wins. If you’re handling employee service requests or dev-related escalations, JSM is a better fit.
Ticketing vs Issue Tracking
- Zendesk uses a traditional ticket management system where each conversation or case becomes a thread, which is tied to customer data and managed through statuses and automations.
- Jira Service Management uses an “issue” model from Jira Software, allowing for highly customizable workflows, fields, and automations that follow development-style logic.
🎯Zendesk is smoother for high-volume, conversation-based support. JSM offers deeper control for process-heavy issue management.
User Experience and Interface
- Zendesk offers a polished, modern UI with low learning curves. Agents can quickly jump into tickets, manage conversations, and access customer history in a unified workspace.
- Jira Service Management’s interface feels more technical. It’s based on Jira’s project-style issue tracking, which is powerful but often overwhelming for non-technical users or customer service reps.
🎯If you need quick onboarding and clean workflows, Zendesk wins. If your users are already Jira-savvy or working closely with engineering, JSM fits right in.
ITSM Capabilities
- Zendesk has limited ITSM functionality. While you can create custom workflows and SLA logic, it’s not ITIL-compliant or designed for complex IT operations.
- Jira Service Management provides out-of-the-box ITSM features like SLAs, incident/change/problem management, on-call scheduling (via Opsgenie), and CMDB/asset management.
🎯For software development teams, JSM is purpose-built. For traditional support, Zendesk remains easier to use.
| Feature | Zendesk | Jira Service Management (JSM) |
| Primary Use Case | Customer support for external users | IT service management and internal support |
| Best For | Customer experience (CX) teams, multi-channel support desks | IT teams, DevOps, and cross-functional internal service teams |
| Ticketing Model | Traditional ticketing with status flows, macros, and views | Jira issue tracking system with customizable workflows and statuses |
| Interface | Clean, intuitive UI built for non-technical support agents | More technical UI built on Jira's development-focused structure |
| Omnichannel Support | Yes. Native support for chat, email, voice, social, web widget | Limited. Basic email intake, some integrations for chat (Slack, MS Teams) |
| Knowledge Base | Zendesk Guide: customizable help center with AI search | Confluence integration: strong internal documentation but not CX-friendly |
| Automation & Workflows | Triggers, macros, SLAs, side conversations | Advanced workflows with Jira Automation, custom rules, and SLAs |
| Reporting & Analytics | Zendesk Explore. Strong out-of-the-box reports, some advanced customizations | Basic reports in free tier, advanced analytics via Jira Premium or 3rd-party tools |
| ITIL / ITSM Compliance | Not ITIL-compliant out-of-the-box | Yes. includes modules for incidents, problems, changes, and service requests |
| CMDB & Asset Management | Not available | Native with “Assets” module (Premium & Enterprise plans) |
| Incident & On-Call Management | Limited | Native integration with Opsgenie – strong on-call scheduling & escalation tools |
| Dev Team Collaboration | Supports side conversations, Zendesk for Jira integration | Seamless handoffs to developers via shared Jira workspace |
| Self-Service Options | Help center, AI-powered suggestions, web widget | Internal service portals via Confluence or Jira Service Catalog |
| Pricing (Starting) | $19/agent/month (Suite Team plan) | $21/agent/month (Standard), $47 (Premium), Free tier available |
| Ease of Setup | Quick to deploy for CX teams | Requires more configuration and setup, especially for non-technical users |
Outdated. Overbuilt. Overcomplicated. Kustomer Fixes All Three.
- Zendesk makes you feel like you need a certified admin just to edit a trigger.
- Jira Service Management assumes every support request is a change ticket or a dev task.
Both are built around systems—not around people.
Kustomer flips that.
It’s designed for modern, high-performing teams who want a single, unified view of the customer and the flexibility to handle support, onboarding, success, and internal ops.
Here’s what you get:
Flexible Workflows Without Developer Headaches
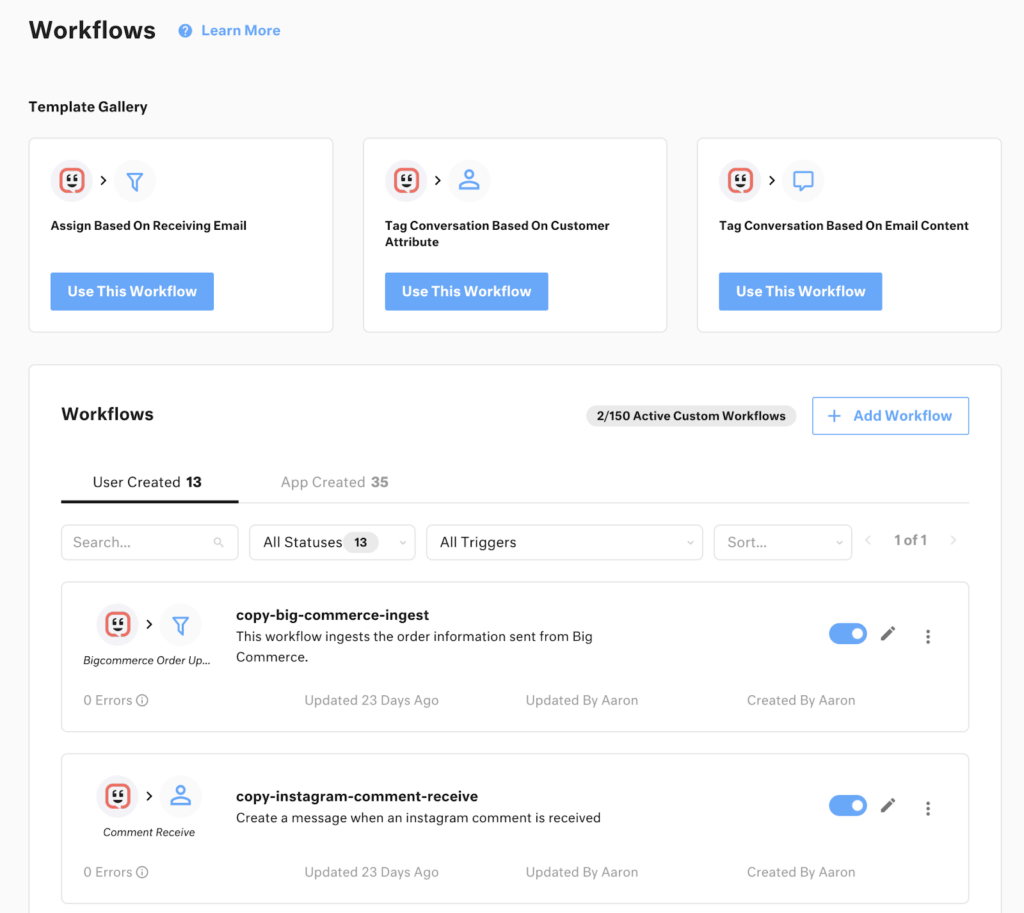
With Kustomer’s no-code workflow builder, you can automate everything from routing to escalations to proactive follow-ups, without writing a line of code.
Need to send an SMS when a VIP files a support issue? Trigger a Slack alert when a competitor keyword is mentioned? All done in minutes.
You don’t need to file a Jira ticket to build a workflow. You can just build it.
Support + CRM in One Platform
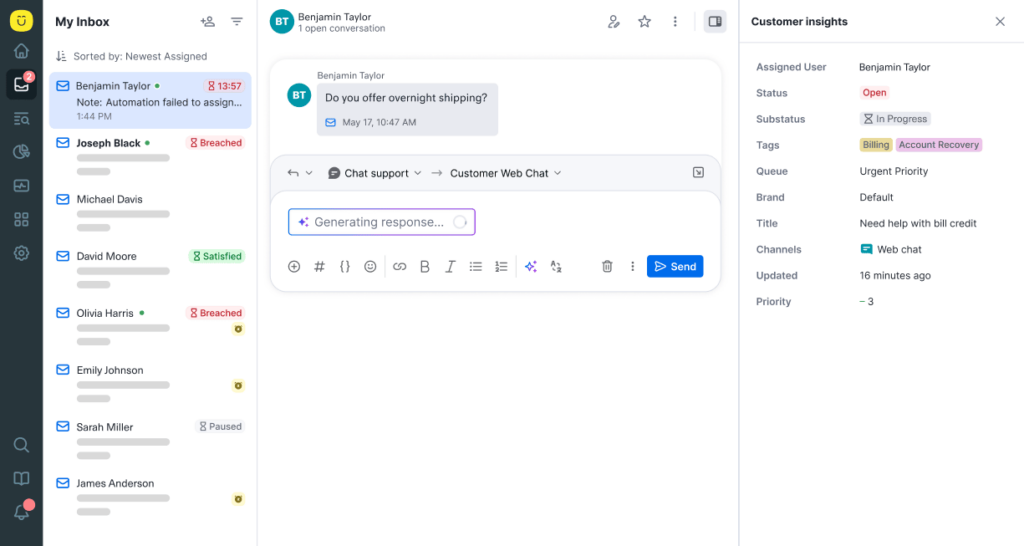
Kustomer doubles as a service CRM, so you’re not integrating multiple tools to achieve a make-shift CRM.
You can store custom objects like subscriptions, orders, devices, plan types—whatever matters to your business—and connect it to every customer conversation.
While Zendesk requires connecting to Salesforce (or its own limited “Sell” product), and Jira requires syncing with Confluence or external CRMs, Kustomer keeps it all in one platform.
Built for Support and Ops, Not Just Dev Teams
Unlike Jira Service Management, which is deeply IT/DevOps-centric, Kustomer is built for frontline support, CX, and revenue teams.
That means intuitive UI, faster onboarding, and features tailored to resolving customer issues, not simply internal tech incidents.
If your business needs to move fast, handle surges, and treat every customer like a VIP—Kustomer’s built for that.
Agent Experience That Reduces Handle Time
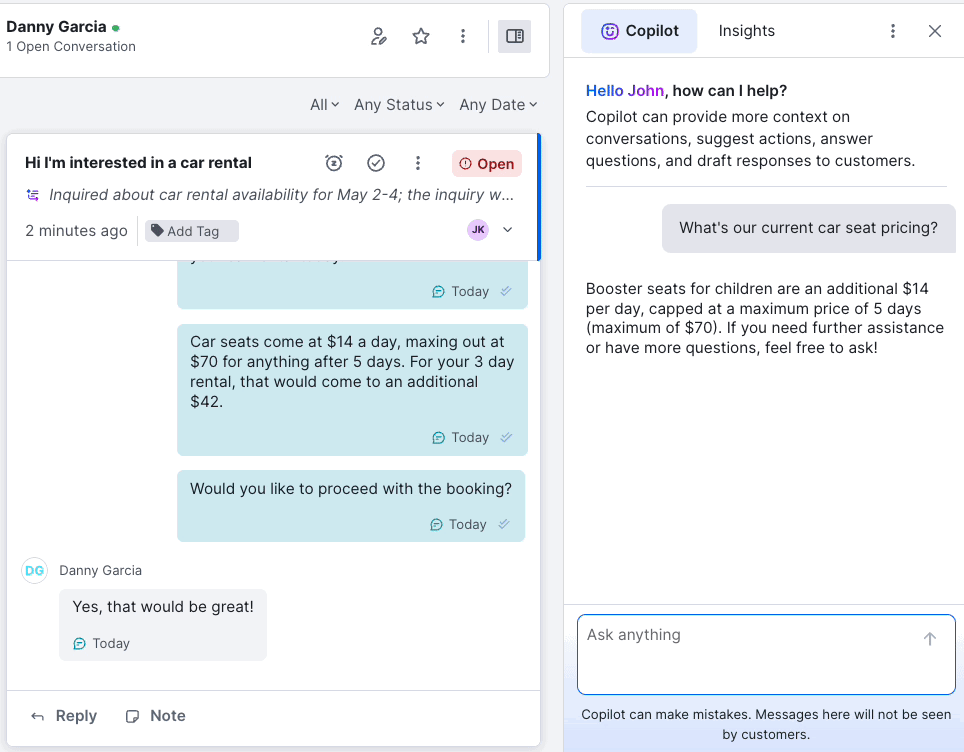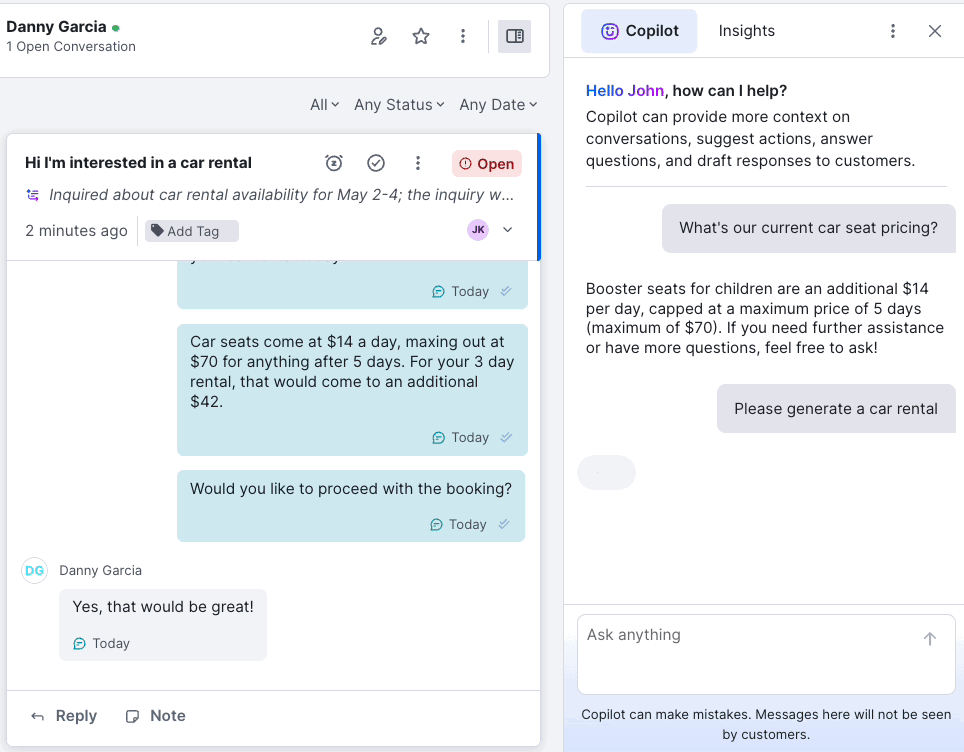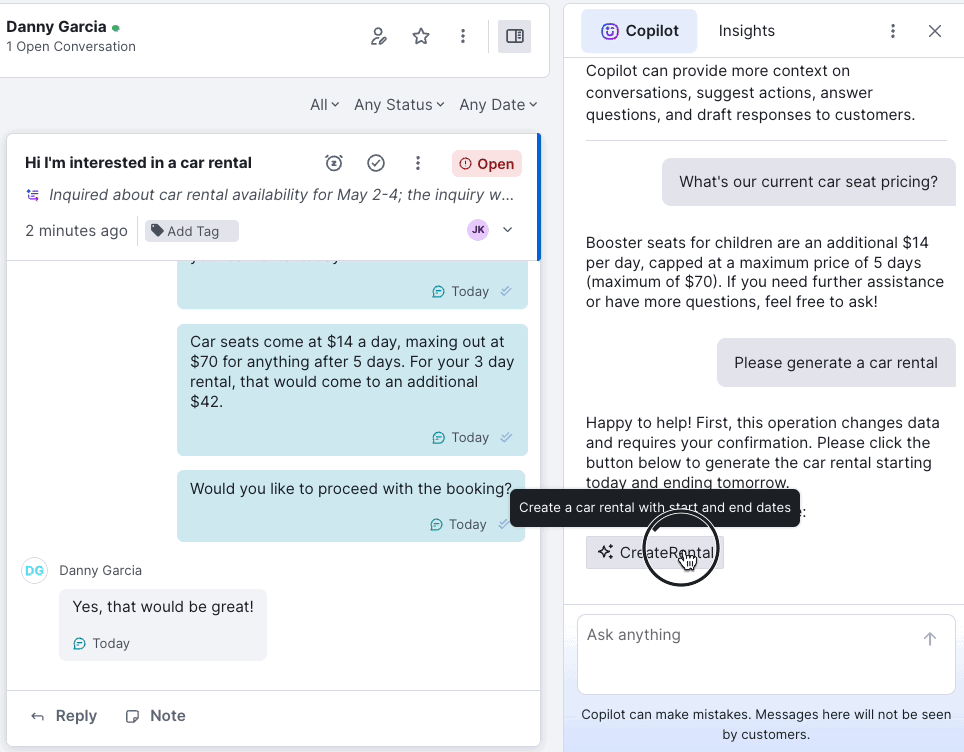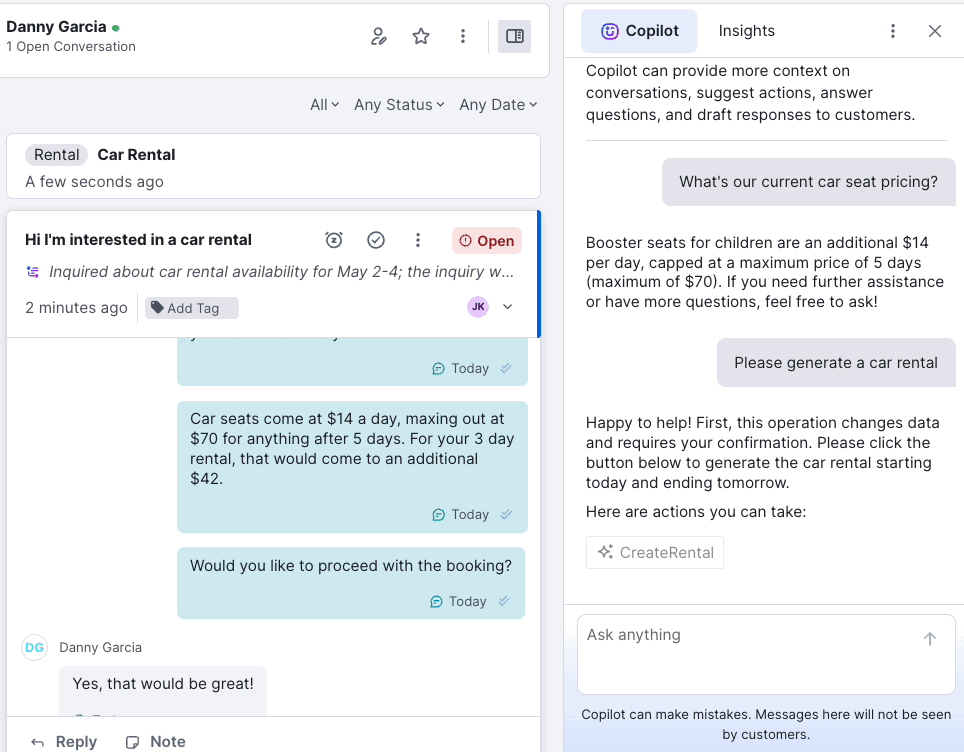
With real-time customer context, a unified timeline, inline notes, AI-suggested responses, and automation baked into the flow, Kustomer agents spend less time searching and more time solving.
Zendesk’s legacy UI requires multiple tabs, back-and-forth lookups, and clunky transitions between apps. Jira’s UX is even more technical, and has a less user-friendly interface for non-IT support agents.
True Omnichannel Support, Natively Unified
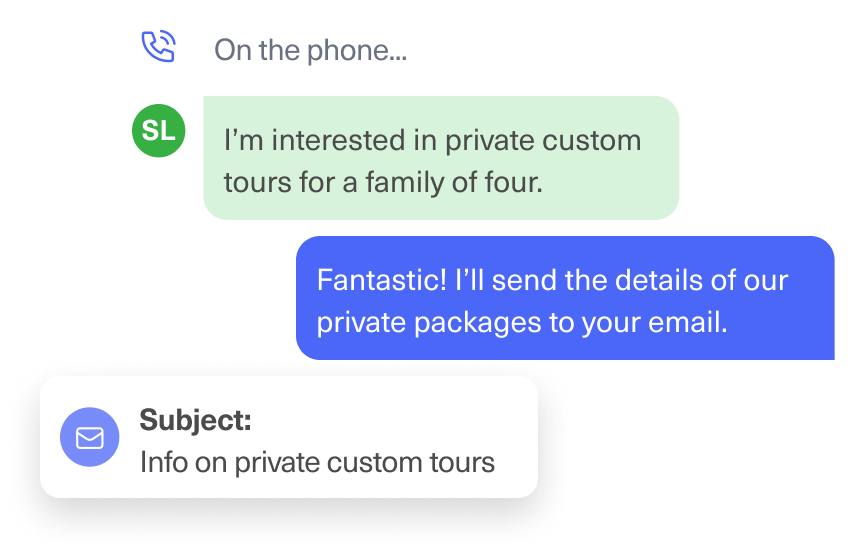
Kustomer was built from the ground up to support email, chat, voice, SMS, WhatsApp, social, and more — all in one workspace.
Unlike Zendesk (which separates channels into modules) or JSM (which barely supports channels beyond email), Kustomer’s omnichannel experience is seamless.
Agents can move between channels without breaking the conversation flow. No duplication, no channel silos, no missed handoffs.
Your Customers Don’t Belong in a Ticket Queue or Kanban Board. Say Hello to Real-Time CX →
Zendesk: Features, Use Cases, Pricing, Pros & Cons
Key Features
- Agent Workspace. Allows agents to manage conversations across email, chat, voice, and social channels—all in one place. It provides a contextual sidebar with customer information, ticket history, and relevant macros.
- Answer Bot. Uses machine learning to suggest relevant help articles based on the customer’s query. It works across chat, email, and the web widget to proactively resolve common issues before reaching a human agent.
- Triggers, Automations & Macros (Workflow Engine). Zendesk offers a robust system for automating support workflows.
- Triggers act on ticket updates (e.g., “if priority = high, assign to Tier 2”),
- automations run on time-based events (e.g., “if ticket is open after 72 hours, escalate”),
- and macros let agents apply canned responses with one click.
- Side Conversations. Agents can initiate internal conversations with other departments (e.g., finance, engineering) without involving the customer. These side threads are linked to the original ticket, keeping all context in one place.
- Sunshine. Flexible CRM layer that allows you to store and manage custom objects (e.g., orders, returns, subscriptions). You can link these objects directly to customer profiles and tickets.
- Flow Builder. A no-code visual editor to build automated conversation flows for messaging bots, helping customers get quick answers or get routed to the right agent.
Main Use Cases
SaaS or Subscription-Based Support Environments
Many SaaS companies can use Zendesk to support ongoing customer success. Agents can track tickets, segment users by subscription tier, automate onboarding emails, and escalate product issues to engineering.
It’s especially effective when integrated with CRMs like Salesforce or HubSpot to sync customer profiles and revenue data.
Global Support Teams Needing Localization
Zendesk supports multi-language ticketing, localized help centers, and timezone-aware SLA tracking, making it ideal for global companies.
Each region can have custom workflows, agent groups, and triggers tailored to local business rules, while still contributing to a global reporting layer. This use case is strong in industries like logistics, hospitality, and telecom.
Support Teams Requiring Collaboration Across Departments
With features like Side Conversations and internal notes, Zendesk makes it easier to loop in sales, billing, compliance, or product teams without losing track of the customer issue.
These conversations stay linked to the ticket, giving full visibility into who said what, when.
Customer Self-Service and Knowledge Management
Zendesk Guide makes it easy to launch and maintain knowledge bases, FAQ hubs, and help centers. These can be publicly available or customer-specific and integrate seamlessly with Answer Bot, Zendesk’s AI-powered suggestion engine.
Zendesk Pricing Plans: What You Get, and What They Don’t Tell You
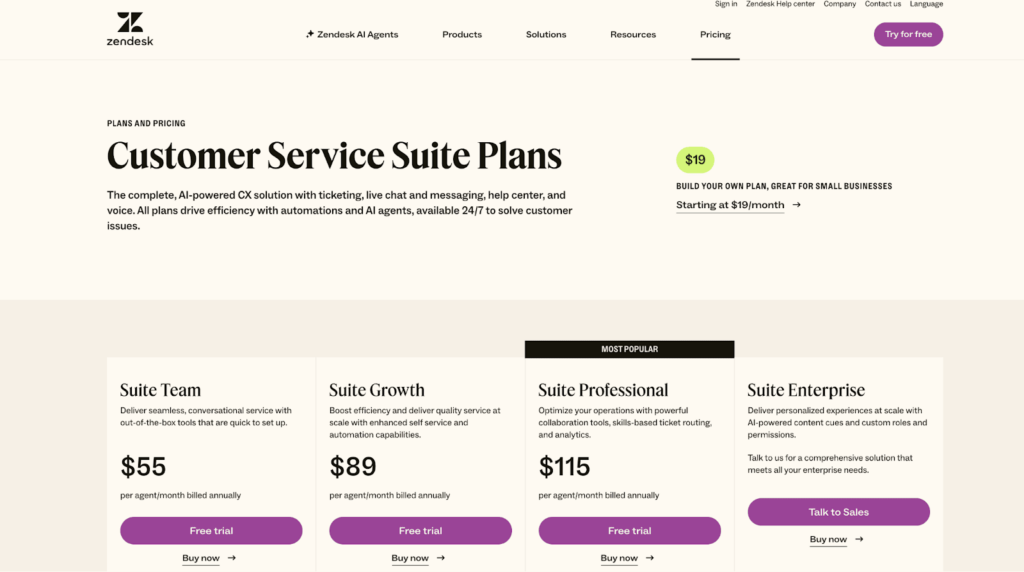
Zendesk offers different pricing options for different business sizes. But for this, we’ll be picking the Suite plan, which covers all major support features.
- Suite Team. $55 per agent/month.
- Suite Growth. 89 per agent/month.
- Suite Professional. $115 per agent/month.
- Suite Enterprise. $169 per agent/month.
- Suite Enterprise Plus. Custom pricing.
Add-ons:
- Copilot. $50 per agent/month for AI-powered tools for agents
- Workforce Management. $25 per agent/month for scheduling and performance tracking
- Quality Assurance. $35 per agent/month for conversation analysis and coaching
- Workforce Engagement Bundle. $50 per agent/month—Combines WFM and QA
- Advanced Data Privacy and Protection. $50/agent/month for enhanced security features.
⚠️What You Don’t See Until After You Buy
- Onboarding Support Is Not Included. If you want Zendesk to help you with setup, training, or success planning, you’ll need to purchase a “Success Plan”. These range from thousands to tens of thousands annually, depending on how much guidance or hands-on support you want.
- Agent-Based Pricing = Rigid and Expensive. Zendesk charges full price per agent. This is regardless of whether that agent is part-time, occasional, or just needs read-only access. There’s no “collaborator” pricing for light users unless you upgrade to Enterprise.
- You’ll Likely Need a Dedicated Admin. Once you start growing (more channels, more automation, custom reporting, brand segmentation), you’ll likely need a dedicated internal or contract Zendesk admin to manage configurations, workflows, and analytics.
- It Gets Expensive Fast at Scale. $115/agent/month sounds manageable; until you have 30 agents, then 50, then 100. Multiply that by additional tools or integrations (like bots, analytics, or CRM syncing), and your support stack becomes a major line item.
🔖 Zendesk’s pricing is layered, modular, and can feel fragmented. What looks like $19 or $55/month on the surface usually turns into a much larger investment once you need real-world functionality, team collaboration, and scalability.
Related reading → Top 20 Zendesk Alternatives & Competitors (Ranked & Rated) | Kustomer
Pros
- Highly Customizable for Growing Teams. Admins can tailor roles, permissions, views, and automations (like triggers and workflows) to match business-specific needs. This makes Zendesk flexible enough for startups and scalable enough for enterprises [*].
- Built-In Collaboration Across Teams. The platform supports real-time collaboration between agents and non-agents, including features like internal notes and live chat handovers. This enhances visibility and promotes cross-team support, especially during escalations [*].
- Integrated Ecosystem. The Zendesk Suite supports advanced automation and multiple use cases under one roof. This serves as both a customer helpdesk and internal knowledge base for distributed teams [*].
Cons
- Limited Out-of-the-Box Sales Integration. Zendesk Sell, the separate CRM/sales product, is widely criticized for lacking functionality. Many teams end up building makeshift solutions inside Zendesk Support to avoid using Sell altogether [*].
- Integration Gaps with Third-Party Tools. Certain integrations (such as with monday.com) are limited to basic ticket syncing. Key actions like bi-directional updates or deep linking remain unavailable, frustrating teams looking for seamless cross-platform workflows [*].
- Complex Email Configuration. Connecting email accounts and managing email flows can be difficult for non-technical users. While powerful, these features aren’t as beginner-friendly as expected [*].
- Lack of Native Round-Robin Routing. Out of the box, Zendesk doesn’t support round-robin ticket assignment. Teams must configure complex skill-based routing or use third-party tools to fill the gap [*].
Related reading → Is Zendesk Worth It? Hmm... See The Pros & Cons
Alternative to Zendesk: Kustomer
Zendesk has been around forever, and it feels like it. Clunky interfaces, stiff ticket workflows, siloed conversations. So it’s basically a relic help desk solution.
That’s why no matter how many add-ons you bolt onto Zendesk — it’s still a ticketing system that separates conversations, systems, and the actual customer behind them.
You end up managing tabs instead of relationships.
Kustomer was built to fix that.
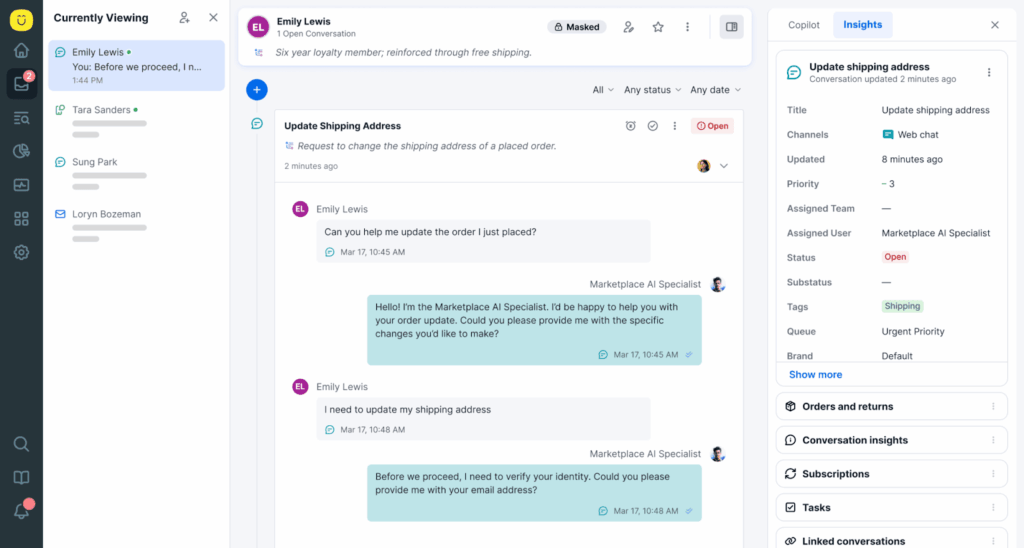
- Designed for the Whole Team, Not Only Agents. With Zendesk, collaboration across sales, support, and ops can feel like playing broken telephone. Kustomer brings your entire team into one platform, with no-agent licensing, real-time notes, and shared views. Everyone’s on the same page.
- Speed to Insight With Built-In Intelligence. Kustomer’s insight gives you instant clarity. You get real-time dashboards, deep drill-downs, and CX intelligence that helps you improve operations.
- Truly Intelligent Automation. Zendesk bots often feel like… well, bots. Kustomer’s intelligent workflows and KustomerIQ automation let you personalize at scale, route smarter, and eliminate repetitive tasks — without sounding robotic or losing that human touch.
If you’re comparing the two, here’s the truth:
- Zendesk is still thinking in tickets.
- Kustomer is thinking in people.
It’s the difference between supporting customers… and actually knowing them.
And for brands that care about long-term loyalty, there’s really no competition.
Case Study → Switching to Kustomer allowed Daily Harvest to scale operations and maintain high-quality customer service

You’ve done tickets. Now do conversations.
Jira Service Management: Features, Use Cases, Pricing, Pros & Cons
Key Features
- Request Types. Lets you create customizable request types (e.g., “Request Access,” “Report a Bug,” “Reset Password”) that map to specific workflows.
- ITSM Processes.
- Change Management (with Risk Assessments). Enables structured workflows for changes, complete with risk evaluation based on historical data, automation rules, and peer review.
- Incident Management. Lets you declare, track, and resolve major incidents with full collaboration capabilities. It includes integrations with monitoring tools and provides timelines, communication logs, and post-incident reviews.
- Problem Management. Help teams identify root causes and reduce recurring incidents. This feature allows linking related incidents, conducting RCA (Root Cause Analysis), and tracking long-term resolution efforts.
- Knowledge Base Integration. Allow customers to self-help using integrated articles from Confluence. Suggested articles appear dynamically during ticket creation to reduce ticket volume and empower users to find solutions.
- Custom Workflows. You can define complex issue transitions (e.g., “Waiting for Change Approval,” “Under Investigation”), assign validators, triggers, and conditions.
- Queues. Allows you to organize and prioritize incoming requests for support teams based on SLAs, labels, priorities, or custom JQL (Jira Query Language). Agents can work from multiple queues and see real-time updates of ticket statuses and workloads.
Main Use Cases
Enterprises Centralizing Service Across Departments
Enterprise teams can use JSM to extend service request management to HR, finance, legal, and facilities. Each department gets its own intake forms, workflows, and SLAs while operating from a shared tool. Examples include PTO approvals, onboarding requests, contract reviews, and vendor access.
IT Teams Running Internal Help Desks
These teams can use JSM to handle common employee service requests like password resets, VPN access, device provisioning, and system troubleshooting.
Employees submit requests via a branded portal or email, and IT agents triage them using prebuilt workflows, SLAs, and approval chains.
Organizations Handling Frequent Change Requests
Companies in healthcare, finance, telecom, or regulated industries can use JSM to process infrastructure or software changes with clear documentation, approvals, and risk assessments.
Teams can also automate approval chains, document reviews, and link changes to releases in CI/CD pipelines.
Companies With SLA Requirements and Audit Trails
Organizations in contract-based industries or those operating under SLA obligations can leverage JSM’s built-in SLA tracking, reporting, and automation to ensure compliance.
Breached SLAs trigger alerts, reports highlight trends, and everything is logged for compliance teams or clients.
Jira Service Management Pricing Plans: What You Get, and What They Don’t Tell You
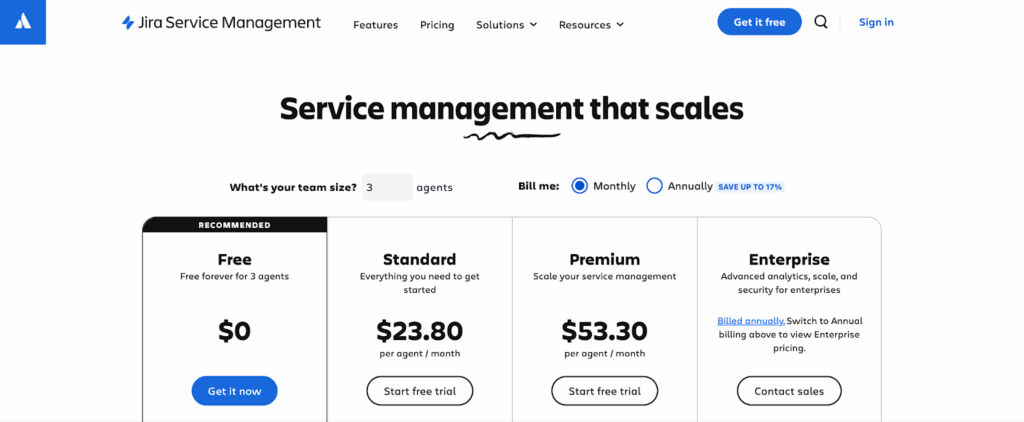
Jira Service Management (JSM) follows a user-based pricing model with tiers that scale in capabilities.
- Free Plan. $0 per agent/month (up to 3 agents)
- Standard. Starts at $23.80 per agent/month (price reduces the more agents you have)
- Premium. Starts at $53.30 per agent/month
- Enterprise. Custom pricing
⚠️What You Don’t See Until After You Buy
- Knowledge Base Requires Confluence. JSM doesn’t include a native knowledge base. To enable self-service, you’ll need a paid Confluence subscription, starting at $5.75/user/month. Multiply that by all agents and possibly other departments—and it adds up fast.
- ITSM Features Are Tier-Locked. Want incident management with on-call schedules? Need asset tracking for devices or software? Those aren’t available in Standard. You’ll need to jump to Premium for those core features.
- Complexity Creeps In Quickly. Setting up JSM properly requires knowledge of Jira workflows, schemes, permissions, and possibly JQL. Even though pricing is attractive, expect to invest time, or hire someone to get it right.
- Collaboration Comes with Limits. If teams outside IT (like HR or legal) need access, you may need additional Jira Software seats depending on how they interact with the tickets and workflows. Atlassian’s pricing model isn’t always transparent here.
🔖Jira Service Management gives you serious ITSM firepower. However, the features most IT teams need (CMDB, incident response, sandbox testing) don’t kick in until the Premium tier. If you’re not a Jira-native org or don’t have admin muscle, it can become a complex (and costly) system to manage.
Related reading → 16 Best Jira Service Management Alternatives Right Now
Pros
- Strong Integrations with Atlassian and DevOps Tools. Seamless connectivity with tools like Bitbucket, Confluence, GitLab, and Opsgenie allows engineering and IT teams to unify service requests, project tracking, and incident management in one place [*].
- Highly Organized Ticketing System. The platform provides structured stages such as To-Do, In Progress, and In Review, making it easy to track progress across multiple teams and projects, particularly in IT or SOC environments [*].
- Cloud-Based Scalability. Jira is built on a scalable cloud environment, offering backend support, custom dashboards, and Slack integrations that support large organizations with cross-functional needs [*].
- Day-to-Day Usability for Tech Teams. For technical users and project managers, Jira supports effective task visibility, approval workflows, and team collaboration—especially for cross-functional and agile development teams [*].
Cons
- Complex Setup and Workflow Design. Setting up custom workflows and configurations often requires technical expertise or developer support, which can slow implementation for smaller teams.
- Limited Out-of-the-Box ITSM Templates. Jira lacks pre-built ITSM processes, making it more of a DIY experience that favors teams already embedded in the Atlassian ecosystem [*].
- Fragmentation Across Projects. ‘Epic’ tracking becomes difficult when multiple team-managed projects are involved, as Jira doesn’t provide a native way to manage shared epics across projects efficiently [*].
- Support and Performance Lag at Scale. Some users report slow response times from customer support, particularly when dealing with large deployments or complex user environments [*].
Alternative to Jira Service Management: Kustomer
If you’ve ever tried offering delightful customer service inside a tool designed for IT teams… you already know the pain.
Your agents aren’t devs. Your customers aren’t tickets. And yet with JSM, everything feels wrapped in red tape, rigid workflows, and an interface better suited for incident reports than conversations.
That’s where Kustomer comes in.
- Faster Setup, Fewer Headaches. JSM’s setup requires custom fields, Jira schemas, and a degree in Atlassian ecosystem. Kustomer offers rapid onboarding and out-of-the-box workflows built for support use cases — not ITIL.
- Smarter Automation Without Developer Dependency. In JSM, even small changes often need admin access or engineering help. Kustomer empowers CX teams with no-code automations, intelligent routing, and conversational bots that you can actually customize.
- Omnichannel > Email-Based Support. JSM is still heavily centered around email and portal requests. Kustomer meets your customers wherever they are — chat, SMS, social, voice, all in one inbox. No juggling channels. No missed moments.
If you’re not running an IT department, stop using IT tools to run your support.
Read Case Study → Food delivery service Jokr/Daki switched to Kustomer for greater configuration flexibility

Leave the sprint boards to the developers. Handle customers with Kustomer →
What to Know Before Choosing Your Next Help Desk Software
Your Support Workflow: Fit First, Features Later
Before comparing features, map out how your support team works:
- Do you handle primarily email-based tickets, live chat, or phone calls?
- How complex are your customer inquiries; are they mostly transactional, or do they span multiple departments?
- How many agents are involved, and what roles do they play (agent, admin, supervisor)?
Once you know this, look for a platform that supports your workflow natively, not one that forces you to change it.
For example, if your team relies heavily on Slack to collaborate internally, choose a tool that offers seamless Slack integration or built-in team collaboration features like internal notes, @mentions, and shared views.
Scalability and Customization Options
Help desk tools vary widely in how well they scale:
- Small teams may prioritize ease of setup and an intuitive UI.
- Mid-market or enterprise teams often need complex workflows, custom roles/permissions, multi-brand support, or robust automation.
Ask yourself:
- Can this platform grow with my business without becoming bloated or overpriced?
- Does it offer modular add-ons, open APIs, or a low-code environment for tailoring processes?
Also, evaluate whether the platform supports custom objects, fields, or ticket types, especially if you deal with industry-specific workflows.
Omnichannel Support Capability
Modern customers expect to reach you across multiple channels: email, chat, social media, SMS, and voice.
True omnichannel support software includes:
- A unified conversation timeline (not fragmented threads per channel).
- Context-aware routing so the right agent picks it up instantly, regardless of entry point.
- Channel-specific SLAs to prioritize what matters most.
Ensure the software can connect all these channels into a single pane of glass experience. This way, your agents aren’t toggling across tabs and your customers aren’t repeating themselves.
Automation, AI, and Self-Service
Great help desk tools do more than organize tickets, they help you solve them faster:
- Automation: Look for advanced triggers, SLA-based workflows, and conditional logic for escalations and assignments.
- AI capabilities: Opt for tools that offer intent detection, sentiment analysis, or suggested responses. This helps reduce handle time and improve response quality.
- Self-service: Evaluate the knowledge base builder, community forums, and chatbot integrations. Bonus points if they let you auto-suggest articles during ticket creation.
A well-designed AI customer service software can deflect up to 30% of tickets, saving time and boosting customer satisfaction.
Reporting, Analytics, and Visibility
Support is a performance-driven function. Choose a platform that helps you:
- Track metrics and KPIs like first response time, resolution time, CSAT, and backlog volume in real-time.
- Drill down by agent, team, channel, or even issue type.
- Schedule and share custom reports with leadership.
Some advanced platforms even offer agent productivity dashboards, forecasting models, or workload heatmaps, giving managers the insight they need to optimize staffing and workflows.
Integration Ecosystem and API Flexibility
No help desk software works in a vacuum. Consider how well it plays with your existing stack:
- CRM (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot)
- Messaging platforms (e.g., Slack, Teams)
- DevOps tools (e.g., Jira, GitHub)
- Billing or eCommerce systems (e.g., Stripe, Shopify)
A strong integration ecosystem or open REST API ensures you can sync customer data, trigger workflows across tools, and avoid manual duplication.
If you rely on a unique internal system, ask about webhooks or middleware compatibility.
Security, Compliance, and Access Controls
Especially for regulated industries (finance, healthcare, legal), your help desk must meet security standards:
- Role-based access controls
- Data encryption at rest and in transit
- Audit trails and activity logs
- GDPR, SOC 2, HIPAA compliance (where applicable)
Ask vendors to provide documentation and support for compliance certifications, especially if you deal with EU/US customers. Also ask about data residency options, incident response protocols, and breach notification SLAs.
Total Cost of Ownership
Licensing is just one piece of the cost puzzle.
Consider:
- Add-on fees (e.g., analytics, automation, AI)
- Implementation or onboarding charges
- Seat pricing vs. concurrent usage pricing
- Cost of third-party integrations or consultants
Sometimes, a tool with a lower monthly fee becomes more expensive when scaled.
Calculate the true cost at your expected scale, and compare that against the value you get in automation, deflection, and faster resolution.
One Timeline. One View. One Reason to Switch to Kustomer
When was the last time a customer said, “Please assign me a ticket number”? Right—never! 🙄
They just want to be heard, helped, and remembered.
But Zendesk and JSM treat every issue like a standalone form submission. You’ve got context bouncing off four platforms, customers stuck in a loop— and agents frustrated.
Kustomer changes all that.
It threads every touchpoint into one living timeline, so every interaction builds on the last.
- No more tab chaos: Agents get full context in a single screen—no toggling between Zendesk, Jira, and Slack to piece the story together.
- Faster resolutions, happier customers: When agents have the full picture, they don’t waste time asking customers to repeat themselves.
Michael Ludwig, Head of Customer Experience at HexClad puts it like this:

Switch now. Smile later.
Because customers deserve more than macros and auto-replies.




