Your customers are everywhere. They email you during work, DM you on Instagram while commuting, and call you when they get home. They don’t see these as three separate conversations; they see them as one continuous interaction with your brand.
But if your support team sees three disconnected tickets, you have a problem.
That’s where Omnichannel CRM comes in. It’s not just about being present on every channel; it’s about unifying those channels into a single source of truth. It creates a seamless experience where context travels with the customer, agents have the full picture instantly, and "Please repeat that" becomes a phrase of the past.
Here is your complete guide to understanding, selecting, and implementing an omnichannel CRM that actually works.
What is Omnichannel CRM?
Omnichannel CRM is a system that helps businesses manage customer interactions across various channels (like email, phone, social media, live chat, SMS, and even in-store) from one central place.
It connects every touchpoint into a single timeline so your team can see the full story of a customer’s journey, irrespective of how or where they reached out.
Think of it like this: Instead of juggling five different inboxes or apps to reply to customers, everything lands in one dashboard. Everyone stays on the same page, and customers don’t have to repeat themselves.
How Does Omnichannel CRM Work?
Omnichannel CRM platforms integrate all customer communication channels into one unified system.
Here’s how it typically works:
- Data Unification. It pulls customer information (name, history, past issues, preferences) from different platforms into a single profile.
- Channel Syncing. Whether a customer sends a DM on Instagram, an email, or calls in; all of those conversations appear in one view.
- Workflow Automation. Tickets get routed to the right agents, messages are prioritized based on urgency or customer status, and follow-ups are scheduled automatically.
- Context Retention. If a customer starts a chat and later sends an email, agents can see both, so they always have full context without asking again.
- Reporting and Insights. It gives managers visibility into customer behavior, channel usage, agent performance, and satisfaction levels.
💡Practical Example
- Let’s say a customer named Sarah reaches out to a fashion brand via Instagram DM about a delayed order.
- Later that day, she follows up via email, and the next day, she calls customer support.
With a regular (non-omnichannel) system, these might look like three separate conversations to three different agents.
But with the omnichannel approach, all three interactions connect to Sarah’s profile.
So when she calls, the agent already sees her Instagram and email conversation without asking her to repeat herself.
It gets even better if Sarah is a VIP customer because the system might automatically push her message to the front of the queue.
Omnichannel vs. Multichannel vs. Single Channel CRM: What is the Difference?
| Feature | Single-Channel CRM | Multichannel CRM | Omnichannel CRM |
| Number of Channels | One | Multiple | Multiple |
| Channel Integration | None | Separate/Siloed | Fully integrated |
| Customer Experience | Rigid | Disjointed | Seamless |
| Agent Workflow | Simple but limited | Fragmented | Unified |
| Context Retention | Minimal | Partial | Complete |
| Best For | Very small teams or solo operators | Growing teams with basic channel needs | Businesses focused on delivering exceptional CX |
Single-Channel CRM: One Channel, One Touchpoint
This is the most basic form of customer relationship management. A single-channel CRM handles customer communication through just one primary channel. This could be email, phone, or in-person support.
How It Works:
Uses a single platform (e,g., email) to talk to customers, and the CRM only logs and manages emails. Every ticket, follow-up, or customer issue happens in that single space.
Example:
A small retailer that only offers support via phone calls might use a CRM to log each customer’s call history and track follow-ups. But if that same customer sends a message on Facebook or Instagram, it’s completely invisible to the CRM.
Limitations:
- No visibility into customer activity outside the single channel.
- Customers have to stick to your preferred channel, not theirs.
- If they switch channels, the context is lost.
Multichannel CRM: Many Channels, But Disconnected
A step up from single-channel, multichannel CRM supports multiple customer touchpoints. But each channel operates independently, like silos. There’s no unified view of the customer.
How It Works:
You can talk to customers on different platforms, but your CRM doesn’t always connect those dots. Agents often switch between tabs or tools to respond on each channel.
Example:
Let’s say a customer reaches out via email, then follows up via Twitter DM. In a multichannel CRM, those appear as two separate conversations. Agents might not know it’s the same person, unless they manually figure it out.
Pros:
- Customers can choose their preferred channels.
- More flexible than single-channel.
Cons:
- Disjointed experiences for customers.
- No full picture of the customer journey.
- Agents might ask customers to repeat themselves.
Omnichannel CRM: All Channels, Fully Connected
This is the preferred standard. Omnichannel CRM connects different channels together into a single, continuous view of the customer.
How It Works:
The system syncs all communication (from email to SMS to WhatsApp to live chat) into one thread. When a customer switches from one channel to another, the CRM stitches those interactions into a unified timeline under one profile.
Example:
A customer starts a live chat on your website, then leaves and sends a follow-up email the next day. With omnichannel CRM, the agent handling the email sees the earlier chat, the customer’s order history, and even their last support ticket.
Key Benefits:
- Complete customer visibility across every channel.
- Seamless handoffs between teams or channels.
- Faster, more personalized experiences.
- Higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
💡Quick Analogy:
Think of it like public transportation:
- Single-Channel is like having one bus route in a city. You only go where the bus goes.
- Multichannel is like having buses, trains, and taxis, but none of them are connected. You have to buy separate tickets and transfer manually.
- Omnichannel is like a fully integrated transit system. One card, one map, every mode of travel synced together.
Benefits of Omnichannel CRM
Seamless Customer Experience
With omnichannel CRM, customers can start a conversation on one channel (like Facebook), continue it on another (say, live chat), and complete it elsewhere (like a call). All of these without having to reintroduce themselves or restate their issue.
The CRM carries context and history across each channel and device in real time.
This level of continuity is impossible with single-channel or even most multichannel systems that operate in silos.

💡Read Case Study → How a Child Rideshare Service Got its CX Team Where it Needed to Go
Improved Customer Loyalty and Retention
When customers feel heard, valued, and cared for across all channels, they’re far more likely to stick with your brand. Omnichannel CRM creates that environment by removing friction and making support feel effortless.
Customers don’t have to explain themselves over and over or suffer from miscommunication between departments. Loyalty also grows because the brand proves it truly knows its customers.
Scalable Support Without Losing the Human Touch
As your business grows, more channels open up—social media, SMS, WhatsApp, voice, chatbots, etc. At this point, the typical traditional system tends to break due to increasing volume.
But with omnichannel tools, automation handles the volume, while your team focuses on high-impact cases. This lets you scale across all channels without losing quality or personalization.
💡 Case Study → Learn how Everlane uses Kustomer to leverage communication with customers throughout the entire customer journey.
“The view of the customer is much more holistic thanks to the Kustomer Timeline. Agents look at the customer as a whole, from purchase history to their interactions, and Tasks make it even easier. The streamlined design and simplicity have made workflows incredibly efficient, which, from a managerial perspective, has been a game changer." — Ashley Julison, Senior CX Specialist, Everlane
Unified Customer View Across All Touchpoints
‘Data unification’ is what makes omnichannel CRM function. It creates a single, centralized profile for every customer, combining all interactions (email, chat, calls, social, SMS, and more) into one clean timeline.
Without it, customer service agents work blind. One rep may respond on email, another on Twitter, and neither knows what the customer already said. With omnichannel CRM, everyone’s in sync, seeing the same full context.
Data-driven Decision Making
Because all customer data flows into one system, you get clearer, more actionable analytics. You can easily track KPIs across all channels, identify bottlenecks, understand channel preferences, and monitor agent performance with precision.
For example, instead of guessing why cart abandonment is high, you can use omnichannel data to see that customers leave when switching from mobile apps to desktop due to login issues—and then fix it.
Better Collaboration Across Teams
Omnichannel CRMs often come with shared inboxes, internal notes, tagging, and handoff features.
This makes it easy for marketing, sales, and support to collaborate on the same customer without overlap or miscommunication.
Support sees the latest marketing promo a customer received. The sales team is aware of past complaints before making a pitch. Everyone’s working towards improving the overall user experience.
Personalized Customer Engagement
With predictive insights and behavior tracking built into omnichannel CRM systems, you can anticipate customer needs before they even express them. You can also tailor conversations based on each customer’s history, behavior, and preferences.
For example, a returning customer asks about a product. The agent knows their last order, sees they left a good review, and recommends a related upgrade—instantly boosting the chance of upsell.
Key Features of Omnichannel CRM
Intelligent Ticket Routing and Queue Management
This is a smart automation feature that ensures customer inquiries go to the right agent or team based on predefined rules like topic, urgency, language, or customer segment.
How it works:
When a message comes in, the system evaluates keywords, metadata (like location or product type), channel, or customer priority level and routes it to the appropriate queue or specialist.
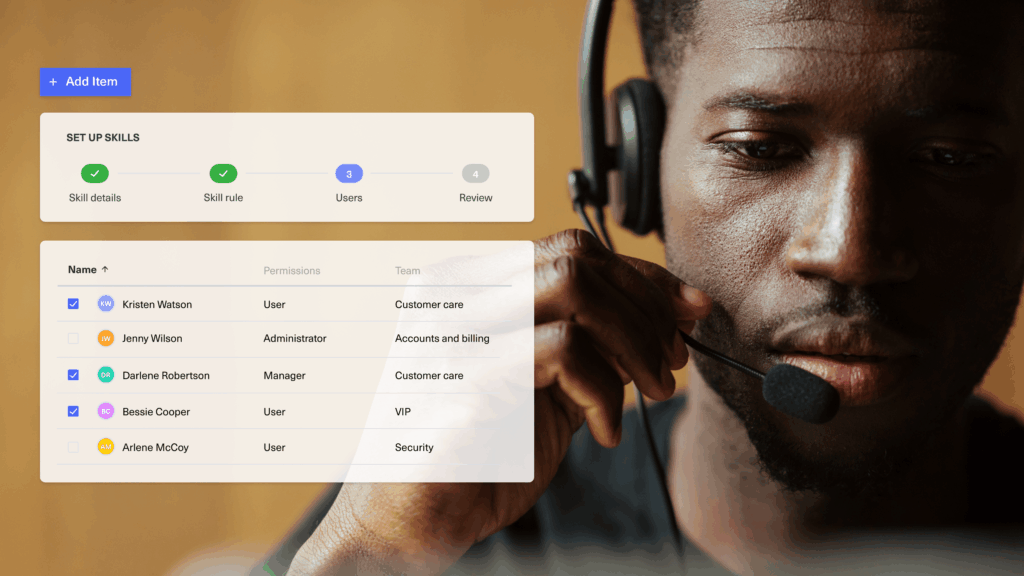
For example, VIP customers might go straight to a premium support team, while technical questions may go to product experts.
Internal Collaboration Tools (Notes, Mentions, Tags)
Built-in tools that allow agents to tag teammates, leave internal notes, or collaborate across departments—without leaving the CRM.
How it works:
- Private notes can be added to a customer thread to give context to the next agent.
- Mentions or assignments let you tag teammates for input or escalate the case.
- Tags and labels categorize cases by topic, urgency, or campaign.
For example, an agent handling a complex refund issue can tag a finance team member, attach an internal note explaining the situation, and loop them in directly.
Unified Customer Timeline
A centralized view that aggregates every customer interaction, ticket, transaction, and engagement across all channels into a single timeline or profile.
How it works:
Every email, live chat, SMS, call transcript, social media DM, support ticket, and note is automatically merged into a single view for each customer.
This creates a full historical record that agents can review before engaging.
Self-Service Tools
Features like knowledge bases, help centers, chatbots, and auto-replies that empower customers to resolve issues on their own (or at least get fast initial help).
How it works:
- A chatbot can guide a user to the right FAQ article.
- Automated workflows send confirmations or follow-ups based on triggers (e.g. “Your ticket has been received”).
- CRMs can integrate with your knowledge base and suggest articles as agents type.
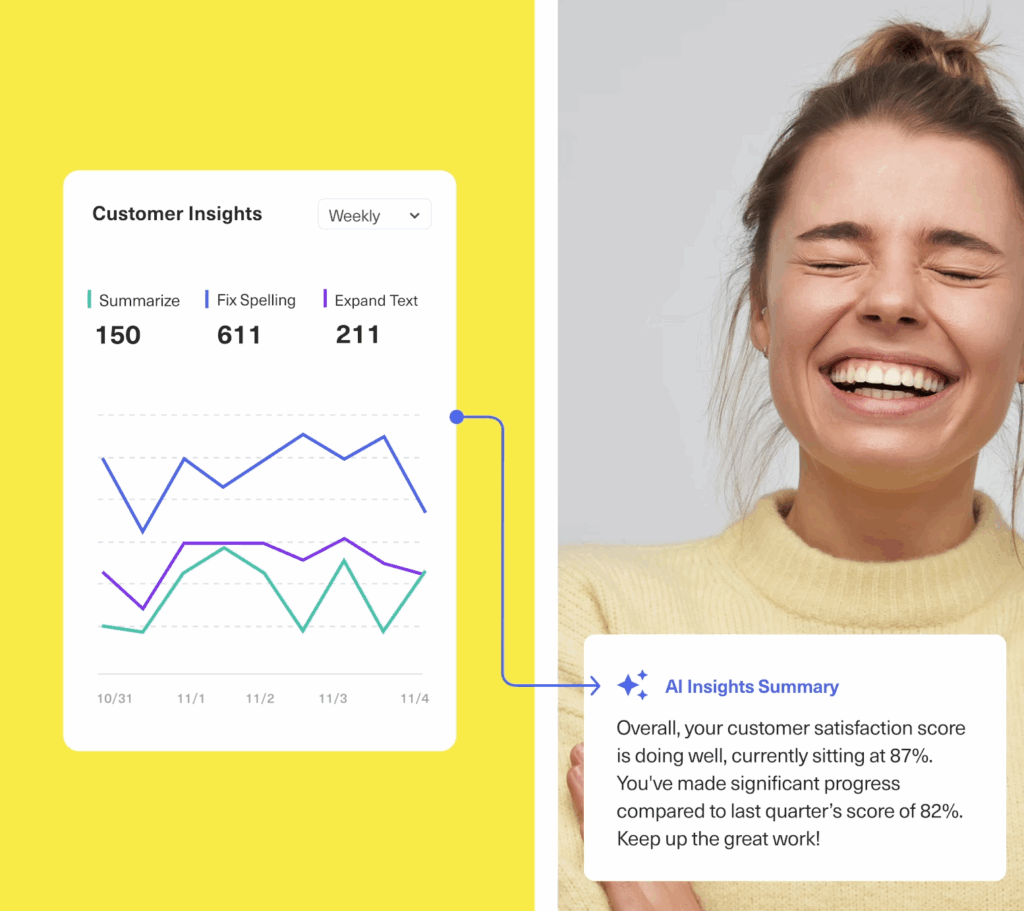
Cross-Channel Analytics and Reporting
Dashboards that give deep insights into customer activity, agent performance, channel usage, resolution times, and overall support trends.
How it works:
Every interaction is logged, time-stamped, and categorized automatically. Reports can be filtered by:
- Channel (e.g. how many tickets came from WhatsApp)
- Agent performance (first response time, resolution time, CSAT)
- Time periods (volume spikes by hour, day, campaign)
- Customer sentiment (based on survey responses or AI tone analysis)
Effortlessly track service performance with Kustomer's live dashboards.
App and Tool Integrations
Pre-built or API-based connections that allow the CRM to integrate with other tools like ecommerce platforms, payment gateways, shipping tools, or marketing automation software.
How it works:
The CRM pulls in data from connected tools, e.g., order status from Shopify, payment history from Stripe, or campaign data from HubSpot; so agents have deeper insight into each customer.
AI-Powered Features
Machine learning capabilities that analyze historical data and real-time behavior to offer suggestions, detect anomalies, and surface insights.
How it works:
The CRM might detect rising frustration in a customer’s messages and prompt the agent to escalate. Or it might suggest upsell opportunities based on recent purchases. AI models learn over time to improve accuracy and relevance.
Customer Data Enrichment
A feature that pulls in additional context about a customer from other tools (e.g. your eCommerce platform, help desk, billing system, or marketing tools).
How it works:
Integrations fetch real-time data like order history, cart activity, subscription status, support level, or survey responses, and display it alongside messages. Some CRMs even use APIs or third-party services to enrich profiles with firmographic or behavioral data.
Implementing an Omnichannel CRM Strategy in 9 Steps
Step 1: Define Your Customer Experience (CX) Goals
Before jumping into platforms or integrations, you need to define a clear vision for what “great customer experience” looks like for your business.
- Are you trying to reduce response times? Improve first contact resolution?
- Provide a more consistent experience across devices and channels? Streamline current business processes?
- Or perhaps gain a unified view of your customer’s journey?
Once these goals are clearly defined, align them with broader business outcomes: customer retention, loyalty, operational efficiency, or customer lifetime value (CLV).
This step will guide every decision that follows, from choosing the best omnichannel solution to designing workflows and training staff.
Step 2: Audit All Current Channels, Tools, and Customer Touchpoints
Next, conduct a thorough audit of every channel where customers engage with your brand.
Go deeper by identifying:
- What tools currently manage each channel (e.g., Kustomer for chat, Outlook for email).
- Where customer data lives (CRM, helpdesk, spreadsheets, eCommerce backend).
- How agents currently access context, or if they’re flying blind across channels.
- Which channels are siloed, causing dropped conversations or duplicated work.
This audit will uncover friction points—like when customers contact support through social media and the agent has no access to their purchase history. Or when multiple agents unknowingly respond to the same issue on different platforms.
Step 3: Select the Right Omnichannel CRM Platform (Fit > Features)
Once you understand your goals and existing ecosystem, it’s time to select a CRM platform that can act as the backbone of your omnichannel strategy.
Look beyond the feature list, and evaluate:
- Channel coverage: Can it natively support the platforms you already use (email, chat, phone, social, SMS)?
- Data unification: Does it create a single customer timeline across channels, or does it only group channels under the same profile?
- Ease of integration: Will it plug into your eCommerce store, help desk, marketing automation platform, and analytics stack?
- Automation capabilities: Can it route tickets, prioritize VIPs, trigger workflows based on rules, and support bots?
- Security and access control: Does it offer granular roles, permission tiers, and audit trails?
💡Pro Tip → Create a shortlist of platforms using real support scenarios (don’t rely on demos alone).
Test what happens when a customer switches from chat to email. See if historical data is carried over. Check if an agent can seamlessly tag a teammate or escalate an issue in-platform.
Step 4: Design Your Ideal Omnichannel Customer Journey
Now that the system is chosen, design the omnichannel experience you want your customers to have.
Start by asking:
- What is the ideal experience when a customer starts on Instagram and switches to email?
- How should the system respond when a VIP contacts us on a weekend?
- At what points should automation assist vs. when should a human step in?
This step requires you to anticipate channel switching, escalations, delays, and customer expectations across devices and time zones.
💡Pro Tip → Build visual journey maps for each scenario (onboarding, complaints, returns, renewals) and include the systems, data, and teams involved.
Then pair every journey with backend actions (routing rules, data enrichment, ticket handoffs). That way, your CRM implementation is directly aligned with the experience you’re designing.
Step 5: Integrate All Communication Channels Into the CRM
This is the technical phase where each customer-facing channel is connected to the CRM to create continuity and context.
For each integration:
- Authenticate the channel (e.g., connect your Instagram Business account to the CRM).
- Set up message routing (e.g., social DMs → social support team queue).
- Enable two-way sync where possible (so responses can be sent from within the CRM).
- Test edge cases: what happens when an image or voice note is sent?
You also need to define the rules of engagement for each channel, i.e., availability hours, tone, SLA expectations, and make sure they’re configured in the CRM settings.
💡Pro Tip → Ensure customer identities are merged across channels. One customer might email from a business address and DM from a personal account.
Your CRM needs to intelligently unify these into one timeline, or agents will lose context.
Step 6: Configure Smart Routing, Automation, and Workflows
With channels in place, the next step is setting up automation logic to ensure messages are routed, escalated, and resolved with minimal delay and maximum relevance.
Start by creating rules for:
- Channel-specific routing (e.g., WhatsApp inquiries go to mobile support specialists).
- Topic-based tagging using keyword detection (e.g., refund requests → billing team).
- Urgency detection (e.g., “angry” tone or VIP customer → escalate immediately).
- SLAs and reminders for response times and ticket aging.
Also, set up automated replies, VIP notifications, status updates, and CSAT requests to standardize communication without overburdening agents.
Step 7: Train Your Teams for Cross-Channel Support and Collaboration
Omnichannel CRM transforms the way support is delivered, so proper training is non-negotiable. Your agents must learn how to use the new system to serve customers across shifting channels.
Conduct hands-on sessions covering:
- Navigating the unified inbox
- Understanding customer timelines
- Using internal notes, mentions, and tags
- When to escalate and how to do it cleanly
- Handling tone and etiquette differences across channels
You should also create role-specific training for supervisors, QA analysts, and reporting teams. This way, they understand how to use the platform to track performance and improve workflows.
Step 8: Launch in Phases With Controlled Pilot Groups
It’s not advisable to roll out your entire omnichannel CRM in one massive go. Instead, launch in phases, starting with a single team, region, or product line.
Begin by:
- Enabling the CRM for a small group of agents
- Limiting initial channels (e.g., email + chat only)
- Monitoring how routing, workflows, and tagging perform
- Gathering direct feedback from agents and customers
Once things are stable, gradually roll out additional channels (like social or SMS), expand to more teams, and tighten integrations with other departments (e.g., sales or marketing).
Step 9: Continuously Monitor, Measure, and Optimize
After launch, your work shifts from configuration to optimization. This is where you extract value from the platform through analytics, feedback, and ongoing refinement.
Focus on performance metrics like:
- Average first response time by channel
- Resolution time per ticket
- CSAT and NPS scores
- Channel volume trends
- Agent productivity and sentiment
Collect qualitative feedback too: What’s still clunky for agents? Where do customers drop off? What feedback are you getting from surveys?
How to Choose an Omnichannel CRM: A Complete Checklist
Does It Support All Your Active and Future Channels?
What to check:
- Email, live chat, SMS, phone, social media (Facebook, Twitter/X, Instagram, WhatsApp)
- Voice support or VoIP integrations if needed
- Bi-directional communication (can you both receive and reply from the same interface?)
Does It Provide a Truly Unified Customer View?
What to check:
- Consolidated timeline of interactions across all channels
- Full profile with customer metadata (order history, tags, feedback, lifetime value)
- Identity resolution for matching conversations across platforms (e.g., email + Twitter)
How Powerful and Flexible Is Its Automation Engine?
What to check:
- Workflow builder with rule-based triggers (e.g., “If tag = billing → assign to finance”)
- SLA timers and reminders
- Automated replies, follow-ups, and escalations
- Integration with bots and AI assistants (e.g., answer common questions or collect data)
Does It Offer Strong Collaboration and Agent Workflow Tools?
What to check:
- Internal notes and agent tagging
- Conversation reassignment or escalation paths
- Shared inbox or queue management
- Collision detection (avoid two agents replying at once)
Does It Integrate With Your Existing Tools and Data Sources?
What to check:
- Native integrations with platforms like Shopify, Magento, Salesforce, HubSpot, Slack, Stripe, etc.
- Open API access for custom integrations
- Webhooks and automation triggers for connected tools
Is the Interface User Friendly?
What to check:
- Clean, organized UI that doesn’t overwhelm agents
- Keyboard shortcuts, smart search, and one-click replies
- Minimal training required to get started
How Safe is Customer Data and Privacy
What to check:
- Ability to assign roles with custom permissions (e.g., view-only, edit, export, admin)
- Audit logs of who accessed what and when
- Data encryption at rest and in transit
- GDPR/CCPA compliance features
What Does the Support, Training, and Onboarding Look Like?
What to check:
- Live chat, phone, or email support availability
- Dedicated onboarding team or self-serve onboarding materials
- Knowledge base, community forums, and learning modules
Does It Scale With Your Team and Business Model?
What to check:
- Seat-based vs. usage-based pricing
- Channel or volume limitations (e.g., message caps, API rate limits)
- Flexibility to grow across departments (e.g., support, sales, success)
Build Loyalty, One Connected Conversation at a Time
And it all starts with Kustomer.
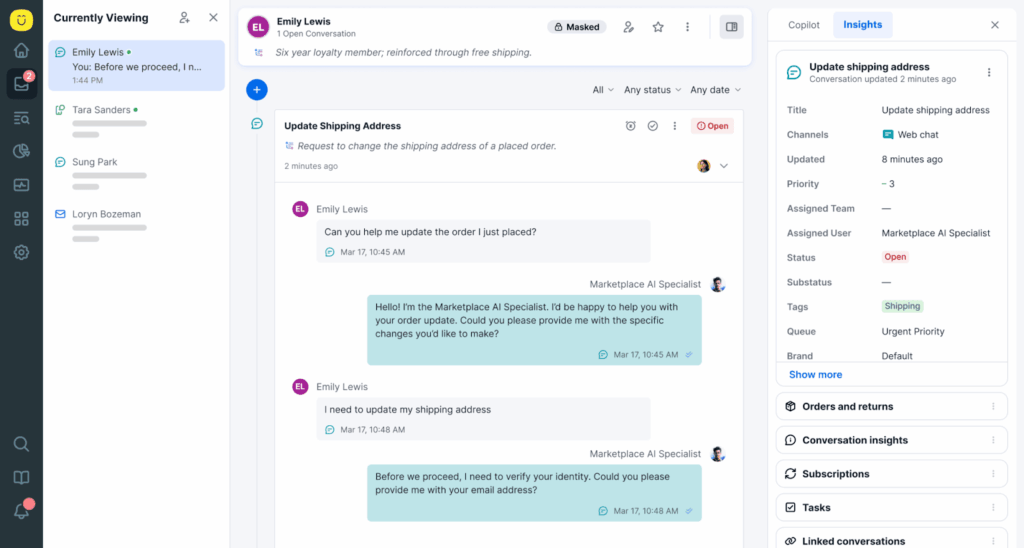
- One Unified Timeline, Zero Repetition. Kustomer gives every agent a complete, chronological view of each customer’s journey—no matter how many channels they’ve used.
- Omnichannel Support, All in One Interface. Whether it’s email, chat, phone, SMS, or social, everything flows into one inbox. Agents don’t switch tabs or tools. They just respond, naturally, with everything they need right in front of them.
- Intelligent Routing That Just Makes Sense. VIP customers go to the right agent instantly. Billing issues route to finance. Urgent messages are prioritized automatically. You never have to triage tickets manually.
- Real-Time Collaboration Without the Clutter. Agents can tag teammates, add private notes, or escalate cases without leaving the conversation.
- Automation That Works Behind the Scenes. With Kustomer, workflows run quietly in the background, handling repetitive tasks, tagging issues, triggering follow-ups.
Plus, if you’re a fast-growing startup or an enterprise with global teams, Kustomer grows with you. It supports new channels, new workflows, and new territories without breaking your system or your team.
Thinking of how Kustomer can also work for you? Listen to what our friends at Vuori have to say:
Switch to Kustomer: Because “Please repeat that” shouldn’t be part of support.

![11 Best AI-Powered CRM Solutions for 2026 [According to Real Users]](https://staging4.kustomer.com/wp-content/uploads/2060/12/ai-powered-crm-solutions.jpg)
![The 10 Best HIPAA Compliant CRM Software for 2026 [According to User Reviews]](https://staging4.kustomer.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/CX-8754751_1280.jpg)
