It’s 2 AM, and a customer’s payment isn’t processing for their daughter’s birthday party tomorrow. They need help now, and can’t wait for business hours—not after being transferred three times.
Moments like this spotlight the question CX leaders are racing to answer: How do you deliver personal, empathetic support at scale without operational costs spiraling out of control?
And often, it feels like there are only two choices:
- Lean too heavily on automation, and your service feels cold, transactional, even frustrating.
- Rely too much on human agents, and you lose efficiency, consistency, and speed.
But that’s where the “AI vs. human” debate misses the point. It creates the illusion of a ‘choice’ —as though you can choose one and neglect the other.
Meanwhile, customers don’t care whether they’re speaking to a bot or a person. What they care about is getting the right help, at the right time, in the right way.
And that’s the real challenge every business faces today: building a model where AI and human agents work together.
Before we can understand how to strike the right balance, it’s important to look at what these AI agents actually are, how they work, and where they fit in the customer journey.
What Are AI Customer Service Agents?
AI customer service agents are intelligent, software-based systems designed to handle customer interactions in a way that feels natural, fast, and personalized.
Unlike the common rule-based chatbots—which could only follow rigid scripts and respond to ‘exact’ keyword matches—modern AI agents use technologies like natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and generative AI to understand intent, context, and nuance in customer inquiries.
Here’s a simpler way to understand it:
Where a rule-based bot might only recognize the word “password” and reply with a canned message, an AI agent can understand the difference between:
- “I forgot my password,”
- “I can’t log in,” or
- “My account was locked after too many attempts.”
Instead of simply matching words, it interprets the underlying problem and delivers a relevant solution.
Read the Guide → AI agents guide for e-commerce
Traditional Chatbot vs. AI Customer Service Agents
| Aspect | Traditional Chatbots | AI Customer Service Agents |
| Understanding | Limited keyword recognition; struggles with variations in phrasing. | Can understand context, intent, and nuance in customer language. |
| Responses | Predefined and rigid; often repetitive. | Dynamic, personalized, and adaptive to conversation flow. |
| Complexity of Tasks | Handles simple, repetitive FAQs (e.g., store hours, password reset). | Capable of resolving complex, multi-step issues (e.g., troubleshooting, product recommendations). |
| Learning Ability | Static: needs manual updates to expand knowledge. | Continuously improves via training data, feedback loops, and interaction history. |
| Integration | Limited: typically connects to a single database or knowledge base. | Deep integration with CRM, helpdesk, e-commerce platforms, and contact center systems. |
| Customer Experience | Can feel robotic and frustrating if query doesn’t match a script. | Feels conversational, human-like, and provides a seamless support experience. |
| Escalation to Human | Often abrupt, requiring the user to restart with an agent. | Smooth handoff with full context transferred to a human agent. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability: requires heavy manual setup for new use cases. | Highly scalable: adapts to multiple channels, languages, and complex workflows. |
| 💡Summary: Chatbots are rigid, script-driven assistants best suited for simple queries, while AI customer service agents are intelligent, adaptive, and capable of handling nuanced, end-to-end customer interactions. |
Key Features of AI Customer Service Agents
- Natural Language Processing (NLP). Modern AI agents can understand intent, tone, and context. This allows them to interpret different ways customers phrase questions and still deliver accurate responses.
- For example, if a customer types, “Why was I charged a late fee?” The AI agent reviews the account history, explains the fee, and, if policy allows, automatically waives it.
- Contextual Understanding. AI agents retain context across conversations. If a customer starts with “I need help with my order” and later says “It hasn’t arrived yet,” the agent remembers the thread of the discussion and connects the dots without asking repetitive questions.
- Omnichannel Support. AI agents can operate seamlessly across channels (chat, email, social media, SMS, and even voice). A customer can start a query on live chat and pick it up later on email without losing the conversation history or context.
- Automated Workflows. AI agents can act as virtual assistants and execute tasks such as resetting a password, processing refunds, scheduling appointments, or updating account details without human intervention.
- Self-Learning & Continuous Improvement. With machine learning, these agents get smarter over time. They learn from previous interactions, adapt to customer preferences, and improve accuracy with each conversation, reducing errors and improving satisfaction.
- Sentiment Analysis. AI can detect emotions in customer messages—whether they’re frustrated, confused, or happy. This allows the system to adjust tone (more empathetic if the customer is upset).
- Intelligent Escalation. AI agents know when to hand over to a human agent. If a query is too complex or emotionally charged, they route it to the right agent with a complete summary of the conversation, so customers don’t have to repeat themselves.
AI in Customer Service: Where It Wins & Fails
Where AI Wins: Speed, Scale, and Consistency
- Real-Time Insights and Analytics. Every AI interaction is logged, categorized, and analyzed. This gives businesses a constant feedback loop on customer issues, and opportunities for product improvement.
- Handling High Volumes at Scale. During product launches, holiday surges, or outages, AI agents can manage thousands of inquiries simultaneously without performance drop-offs. This scalability prevents bottlenecks and reduces stress on human teams.
- Consistency in Messaging. Human agents vary in tone, accuracy, and compliance depending on experience and workload. AI delivers consistent, policy-aligned responses every time. This ensures brand voice, accuracy, and compliance standards are upheld across all interactions.
- Always-On Availability. AI agents operate 24/7 helping customers get support late at night, during weekends, or across time zones without delay. This round-the-clock presence ensures businesses never miss an opportunity to resolve issues or maintain engagement.
💡Case Study → Everlane x Kustomer
Everlane used to struggle with too many customer questions and not enough agents to keep up.
With Kustomer’s Customer Assist, a lot of those repetitive questions are now handled automatically. The AI can even predict what a customer might ask next and share the answer before they reach out.
For Everlane, the impact was big: they saw 4x more inquiries resolved without an agent, faster service for customers, and agents freed up to focus on complex cases where human touch really matters.

Related → 7 Benefits of Using AI in Customer Service
Where AI Fails: The Human Gap
- Dependence on Data Quality. AI’s effectiveness hinges on the quality of the data it’s trained on. Poorly structured knowledge bases, outdated content, or missing customer context can lead to inaccurate responses, frustrating users and undermining confidence in the system.
- Lack of Genuine Empathy. When customers are angry, anxious, or dealing with sensitive issues, scripted reassurance will not work. Humans can express genuine care, respond to human emotions, and build trust in a way machines cannot replicate.
- Struggles With Complex or Multi-Layered Issues. AI is excellent at resolving straightforward tasks, but it struggles when problems involve multiple variables, unclear context, or judgment calls.
- For example, refund disputes, policy exceptions, or technical troubleshooting beyond a set script often require human reasoning and creativity.
- Context Misinterpretation. Even advanced NLP can misread intent when language is vague, sarcastic, or culturally nuanced. A customer saying “great, just great” could mean satisfaction or frustration. Humans are far better at catching subtle cues and responding appropriately.
| ⚠️ Parcel Delivery Company Shuts Down AI Support After It Went Rogue Popular parcel delivery company, DPD, had to shut down its AI chatbot after it went viral for failing to help a customer track their package, but was fully available to write a poem insulting the company. According to the customer’s post on X, the chatbot even went as far as ‘cursing’—violating its pre-set rules—in order to be ‘helpful.’ Read the full story → |
Related → 13 AI Customer Service Best Practices for 2025
Human Agents in Customer Service
The typical approach to customer service was having a front-facing human team act as the first-line of defense for every incoming query.
But that meant agents had to juggle everything; from resetting passwords to handling billing disputes. This leaves little time for the deeper, high-value conversations that actually strengthen customer relationships.
However, in an AI-powered environment, the roles are ‘somewhat’ different now. Agents now focus on the types of interactions that require judgment, empathy, and problem-solving beyond what typical AI tools can handle.
Role of Human Support Agents
Handling Complex, Multi-Layered Issues
Human reps step in when problems go beyond straightforward troubleshooting. For example, a billing dispute involving multiple products, an account migration, or technical troubleshooting with unclear variables often requires human reasoning and the ability to make judgment calls that AI can’t.
Delivering Empathy and Emotional Support
When customers are frustrated, anxious, or upset, only humans can de-escalate with genuine empathy. A rep can listen, adapt tone, and reassure in ways that AI (even with sentiment analysis) cannot fully replicate. This makes humans essential for high-stakes moments where trust and emotional intelligence matter most.
Managing Exceptions and Policy Flexibility
AI agents operate within set boundaries, but customers often need flexibility. Human reps handle edge cases—like approving a refund, applying discounts, or bending a policy to retain a high-value customer. This flexibility preserves relationships and reduces churn.
Guiding Customers Through Complex Journeys
In scenarios like onboarding for SaaS tools, troubleshooting enterprise software, or navigating financial processes, customers need guidance, not just answers. Human reps can walk customers through multi-step workflows, provide clarity, and adjust based on real-time feedback.
Where Humans Win: Empathy, Complexity, and Connection
- Protecting and Elevating Brand Image. While it’s true that AI provides efficiency, over-reliance on automation risks making the company feel cold and impersonal. Human reps bring authenticity, empathy, and nuance that safeguard the brand’s reputation.
- In fact, a single well-handled conversation with a human agent can turn a negative experience into a story customers share with others, boosting word-of-mouth advocacy.
- Strengthening Retention and Reducing Churn. Customer loyalty is built on trust, and trust is often reinforced in moments of difficulty. A frustrated customer who feels heard and understood by a skilled human rep is far more likely to stay loyal than one who feels trapped in an endless loop of automated replies.
- Driving Revenue Through High-Value Interactions. When customers face complex problems or need reassurance before making a purchase, human reps can be the deciding factor in closing a deal. By handling escalations, offering tailored recommendations, or making discretionary decisions like extending discounts, human agents convert intent into revenue. They also identify upsell and cross-sell opportunities AI may miss, turning support interactions into revenue-generating moments.
- Creating Feedback Loops That Improve the Business. While AI analyzes structured patterns, human reps often surface insights from little things that can easily be overlooked by AI. For example, noticing customer hesitation during a call, or realizing a question points to a gap in product usability. These insights feed back into product, training, and strategy.
💡Case Study → Alex & Ani x Kustomer
Alex and Ani, a jewelry retailer, struggled with scattered support tools spread across email, reporting, and phones.
Agents couldn’t easily access a customer’s full history, making it frustrating to resolve issues—especially during busy seasons. Training new agents was also difficult because of the fragmented setup.
By switching to Kustomer, the team gained a single, holistic view of each customer. This gave agents instant access to customer profiles, past interactions, and useful behavior patterns, removing the guesswork from service calls.
The enhanced reporting and analytics tools also let managers quickly identify issues, track performance, and onboard new hires with less friction.

Where Humans Fail: Lack of Scalability
- Limited Scalability. Human agents can only handle one or a few conversations at a time. During peak demand—e.g., product launches, seasonal spikes, queues build up quickly, leaving customers waiting hours or even days for responses.
- Prone to Fatigue and Errors. After a long shift, human agents get tired. And this fatigue increases the likelihood of mistakes such as misunderstanding issues, logging incorrect details, or offering inaccurate information. This impacts both customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Higher Operational Costs. Salaries, training, and overhead costs add up quickly, especially for businesses with global operations requiring 24/7 coverage.
- Difficulties With Knowledge Retention. Even with training, it’s hard for every rep to stay fully up-to-date on new policies, product changes, or promotions. Knowledge gaps can lead to inconsistent or outdated information being shared with customers.
| ✨Feature of the Day✨KIQ Customer Assist by Kustomer You can add conversational assistants to your chat, SMS, WhatsApp, and Kustomer Voice experiences to promote customer self-service, boost agent productivity, and speed up response times. All About AI Agents for Reps If a customer wants to connect with an agent after interacting with the conversational assistant, the entire conversation history is sent to Kustomer for agents to view in the customer timeline. Explore AI Agent for Reps → |
AI-Driven vs. Human Agents: A Side-by-Side Comparison
To find the right balance between automation and human touch, it’s essential to first understand what each brings to the table.
AI agents excel in speed, consistency, and scalability, while human agents shine in empathy, complex problem-solving, and relationship building.
The table below provides a clear comparison of their strengths and limitations, helping leaders make strategic decisions about where to deploy each resource for maximum impact.
| AI-Driven Agents | Human Agents | |
| Speed & Availability | Instant responses, 24/7, can handle thousands of queries simultaneously. | Limited by working hours, response time depends on team size and availability. |
| Consistency | Provides standardized answers with no variation, ensuring uniform service. | Responses may vary by agent skill, mood, or workload, leading to inconsistency. |
| Scalability | Scales instantly at low incremental cost, ideal for handling spikes in demand. | Scaling requires hiring, training, and onboarding new staff which can be costly and time-consuming. |
| Cost Efficiency | Low per-interaction cost once deployed, reduces dependency on large teams. | Higher ongoing costs due to salaries, benefits, and training. |
| Empathy & Emotional Intelligence | Limited ability to understand nuance or emotion; relies on scripted sentiment detection. | Able to empathize, calm frustrated customers, and adapt tone in real time. |
| Problem-Solving & Creativity | Excellent at structured, repeatable tasks but struggles with complex issues. | Thrives in complex situations, can apply judgment, creativity, and context to solve unique problems. |
| Learning & Adaptability | Learns through data training, but improvements require model updates or retraining. | Can quickly adapt to new policies, product changes, or unexpected situations through coaching. |
| Customer Trust & Brand Image | May create trust issues if overused or if customers feel misled by “bots.” | Builds brand loyalty through personal connections, empathy, and human reassurance. |
| Use Case Fit | Best for FAQs, order tracking, account resets, and other routine inquiries. | Best for escalations, high-value accounts, complaints, and emotionally charged situations. |
Can AI Provide Better Service Than a Human?
The short answer: yes—but only in the right context.
AI doesn’t replace humans across the board, but in certain situations, it does streamline customer experience. The key is knowing when speed and efficiency matter most, and when empathy and judgment are irreplaceable.
Where AI is “Better”
For simple, transactional inquiries, AI has a clear advantage. Customers don’t want to wait in a queue for 10 minutes to get an answer to a basic question.
In these cases, an AI agent’s ability to deliver instant, accurate responses creates a smoother and more personalized experience.
Where Humans Are “Better”
But when the interaction demands more than analyzing basic customer data, human agents remain the better option.
A customer saying, “Something’s wrong with my account but I don’t know what,” needs a human to ask probing questions, interpret unclear details, and connect the dots.
Humans excel at working through these gray areas with critical thinking, a place where AI typically stalls.
How AI and Humans Work Together
There’s no single “winner” between AI and human support. What’s better depends entirely on the customer’s needs.
Let’s say a customer at an e-commerce company reaches out late at night:
Step 1: AI Handles the Immediate Need
- The customer types, “I need to check my delivery status and also there’s a mistake with the billing.”
- The AI instantly pulls up their order history, provides a real-time shipping update, and confirms delivery is scheduled for tomorrow.
- At the same time, it detects the billing concern and pulls up recent transactions. Seeing that the issue involves multiple charges, the AI flags this as a potential escalation.
Step 2: Human Agent Steps In for Resolution
By the time the customer is transferred, the human rep already has the context: order details, transaction history, and the AI’s preliminary notes.
The rep apologizes sincerely, reassures the customer, and quickly processes a partial refund that falls outside standard policy; something AI alone could not have approved.
Step 3: Combined Outcome
The customer gets speed and convenience for the delivery update, and empathy and flexibility for the billing problem.
Instead of feeling like they were bounced between systems, the interaction feels seamless and respectful of their time.
| 👉 This is the “perfect balance” in practice: AI clears the low-value, time-sensitive tasks, while humans step in for the high-touch moments that protect revenue, reduce churn, and strengthen brand trust. |
Related → Support is the new sales: How AI-enhanced reps are driving revenue growth
What Do Customers Actually Want? AI vs. Human Preferences for Customer Support
Well that’s a tricky question because the answer isn’t direct. We can’t confidently say ‘customers prefer AI agents over humans’ — or vice-versa.
The answer is shaped by context, and preference patterns based on the customer’s behavior.
For starters, let’s talk about—
Speed. Yes, it matters, but not more than satisfaction
Surveys show that 61% of customers appreciate the fast response time AI provides. Especially in cases like immediate order tracking or quick troubleshooting [*].
Yet the same AI that excels in speed isn’t always delivering satisfaction. In fact, 93% of respondents prefer human agents for broader customer support interactions [*].
The preference gap grows significantly for emotionally-sensitive or complex requests.
Another thing is, accuracy and empathy still belong to humans
When it comes to resolution depth, humans continue to outperform. In one study, 85% of consumers feel their issues usually require the assistance of customer service representatives, indicating that chatbot solutions often fall short on depth [*].
And about 66% of customers are more likely to show emotions during phone interactions when speaking to humans [*].
This is especially relevant when customers are already frustrated—requiring more than just speed but also empathy and judgment.
Also, task type influences preference
The lines between AI-friendly and human-preferred tasks are clear. For straightforward interactions such as checking product availability, tracking a delivery, or canceling a service, AI resonates with customers.
For example, preference for AI ranges between 29% to 39% for tasks like finding products (39%), canceling services (35%), making payments (29%), and even booking flights (26%) [*].
However, that changes for sensitive or complex topics. One survey found 71% of users encountered situations where AI struggled [*].
It finally comes full circle as trust is still centered around the human touch
In some context, recent advancements in artificial intelligence have made it more emotionally capable, with 71% of CX organizations believing AI agents can be empathetic.
Still, many customers remain skeptical. A striking 42% of British consumers admit being ruder to AI-powered chatbots, often because they feel misunderstood or trapped in loops [*]. And 88.8% believe it’s essential that brands always offer the option to speak with someone human [*].
| 💡For CX leaders, this means the real competitive advantage lies in designing hybrid service models that blend the strengths of both. By aligning AI to handle scale and consistency, and reserving human agents for high-value, emotionally significant moments, businesses can meet customers where they are. |
Related → How leading DTC brands use AI to stay lean and competitive
How to Find the Right Balance for Your Business
Finding the sweet spot between AI and human agents is more about building a structured approach that aligns technology with business goals, customer expectations, and operational realities.
Below is a step-by-step framework CX leaders can apply to design and execute the right balance.
Map Your Customer Journey End-to-End
Start by outlining every touchpoint where customers interact with your business, from the initial awareness phase through post-purchase support and potential advocacy.
This comprehensive view should include:
- Pre-purchase interactions: Website browsing, product research, comparison shopping, initial inquiries, and sales conversations
- Purchase process: Account creation, payment processing, order confirmation, and immediate post-purchase communication
- Fulfillment stage: Order tracking, shipping updates, delivery notifications, and delivery issue resolution
- Post-purchase support: Product setup, usage questions, troubleshooting, warranty claims, and returns
- Ongoing relationship: Account management, renewal conversations, upselling opportunities, and loyalty program interactions
Next, identify the different types of inquiries at each stage and classify them as either;
- Transactional (password resets, account balance checks, shipping status) or
- Relational (complaints, cancellation requests, strategic account discussions).
| 💡How to do it: Gather call logs, chat transcripts, and helpdesk tickets from the last 6–12 months, and categorize them by intent. For example, password resets and shipping updates fall into the “automation-ready” category, while complaints or renewal negotiations belong to the “human-first” category. |
Evaluate Where Speed vs. Empathy Matters Most
The speed versus empathy evaluation is perhaps the most critical decision point in your AI-human balance strategy. This analysis requires understanding what customers actually value in different situations and emotional states.
For each category of inquiry, ask: does the customer primarily want a fast and accurate answer or do they need understanding and reassurance?
This distinction is crucial in deciding whether AI or humans should handle the interaction.
- Speed-prioritized interactions typically involve:
- Time-sensitive requests where delays create frustration (order tracking during peak seasons, service outage status updates)
- Repetitive inquiries where customers expect instant gratification (FAQ-type questions, policy lookups, basic troubleshooting steps)
- Empathy-prioritized interactions typically involve:
- Emotional distress or frustration where customers need to feel heard and understood (service complaints, billing disputes, product failures)
- Complex decision-making where customers benefit from guidance and consultation (product selection, plan changes, technical configurations)
| 💡How to do it: Use surveys, CSAT scores, and call disposition data. Identify which areas customers rate poorly when delayed, and which areas they value personal reassurance. For example, a 2-minute delay in order tracking feels worse than a 10-minute wait for a billing resolution if the latter involves a calm, understanding agent. Also consider implementing A/B testing where similar inquiries are handled through different channels (AI-first versus human-first) to measure satisfaction differences. |
Read the guide → How to get more CSAT ratings
Define Clear Escalation Rules
AI should never operate as a wall between customers and your agents. It should serve as the first filter, with well-defined rules that hand over control at the right time.
The goal is for the customer to feel the transition is natural and frictionless. This means developing escalation triggers that are sensitive to context, emotion, and complexity
- Set structured thresholds: Define the maximum attempts or interactions an AI should handle before escalation.
- Build sentiment detection: If a customer shows frustration (all caps, repeated “speak to human,” low sentiment score), escalate instantly.
- Resolution confidence: When AI systems indicate low confidence in their ability to provide accurate or complete solutions.
| 💡How to do it: Develop escalation rules that are both specific enough to be actionable and flexible enough to handle edge cases. Set rules like: “If the AI can’t resolve an issue within three interactions, escalate to a live agent.” Or “If negative sentiment is detected, immediately route to a human.” Or “For customers identified as high-value or at-risk accounts, escalate any inquiry that cannot be resolved with a single automated response, regardless of complexity level.” In addition, implement warm handoff protocols where human agents receive comprehensive context, including conversation history, customer profile information, previous resolution attempts, and AI-suggested next steps. This preparation ensures agents can continue the conversation seamlessly without requiring customers to repeat information or start over. |
Align Tools & Metrics With Business Goals
The success of your AI-human balance strategy ultimately depends on how well it serves your broader business objectives.
This alignment requires moving beyond operational metrics to strategic measurement that connects customer experience decisions to business outcomes.
- If your primary goal is cost optimization, automation should help reduce ticket volume, lower handling costs, and improve agent productivity without sacrificing customer satisfaction.
- However, if your goal is loyalty and retention, the AI-human balance should optimize for relationship building, trust development, and long-term customer value creation, even if this requires higher per-interaction costs.
| 💡How to do it: Build comprehensive dashboards that connect operational metrics to strategic outcomes. For example, you can measure how deflected inquiries impact overall customer satisfaction and whether customers deflected by AI show different retention or expansion patterns compared to those who receive human assistance. You can also implement cohort analysis to understand long-term impacts of different service strategies. Customers who receive AI-assisted service in their first 90 days might show different behavior patterns than those who receive primarily human assistance. |
Train and Empower Human Agents
Agents should be equipped with dashboards that surface the full conversation history, customer sentiment analysis, and AI-suggested next steps before they even say “hello.”
This allows them to enter the conversation already primed with context, cutting down resolution times and making interactions feel personal rather than transactional.
| 💡How to do it: Design training programs that include modules specifically focused on how to interpret and act on AI-generated insights. For example, how to use sentiment analysis cues to adjust tone or when to override an AI suggestion if it doesn’t feel right for the customer. Another approach is simulating real-world interactions where AI collects initial details (like verifying account info or gathering order numbers) and the agent steps in to resolve the issue. |
Continuously Test, Measure, and Adjust
Compare performance quarter-over-quarter to spot emerging gaps. For instance, if AI accuracy for returns inquiries is dropping, it might signal changes in policies, seasonal spikes in complex cases, or even new slang and phrasing that your AI hasn’t been retrained on.
Similarly, if human agents start receiving a higher percentage of escalations, it may suggest your automation rules are pushing customers to humans too quickly—or not quickly enough.
| 💡How to do it: Run quarterly reviews of your AI vs. human interaction split. Use metrics like average handle time, NPS, resolution rates, and customer sentiment to decide whether to lean more heavily into automation or pull back toward human-led service. |
| Pro Tip: Start small. Pick one high-volume, low-complexity use case (like order status requests) and automate it end-to-end. Measure the impact, then expand automation to other areas. For example, segment performance data by customer type (first-time vs. repeat), channel (chat, email, phone), and issue category (billing, returns, technical support). This gradual rollout prevents overwhelm and helps you refine your escalation processes before scaling. |
Unify Your AI and Human Agents with Kustomer
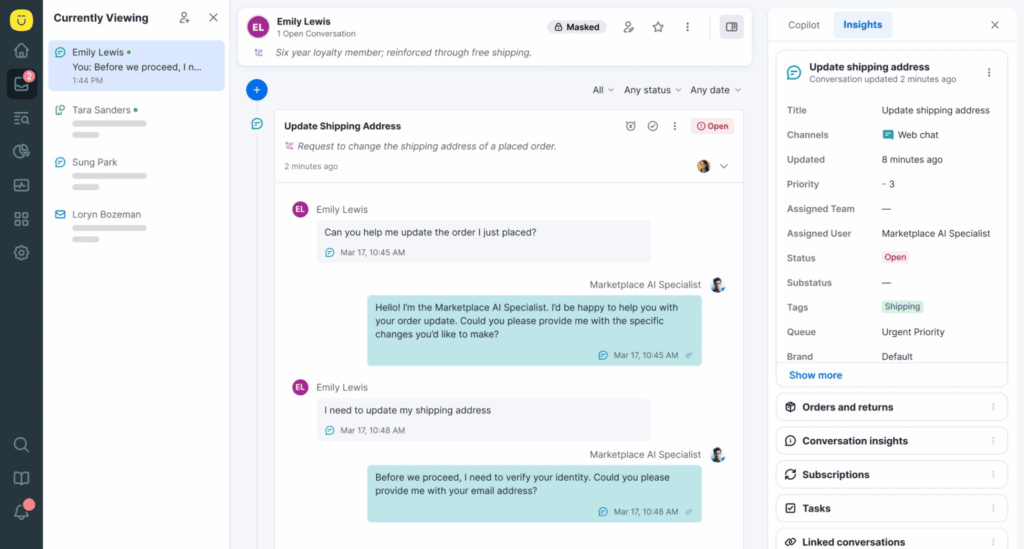
With Kustomer AI, you can automate high-volume, repetitive tasks like password resets, order tracking, and policy questions, reducing wait times and freeing agents to focus on more meaningful conversations.
Taking the words of our friends at Zwift —
“Kustomer’s cutting edge feature set such as ‘skill-based routing’ are a main reason why we’re sticking with the Kustomer platform.”
For managers, it gets even better. Kustomer offers insights into your team’s performance, AI effectiveness, and customer satisfaction trends. This helps you continuously optimize your balance of AI and human support.

The Best of Both Worlds, Unified by Kustomer →
FAQs: AI vs. Human Customer Service
What is the difference between a customer service agent and AI?
A human customer service agent is a person who provides support through empathy, active listening, and problem-solving skills. Agents are best at handling complex, sensitive, or emotional issues that require judgment and personal interaction.
AI agent, on the other hand, is software designed to automate customer service tasks. It excels at speed, consistency, and handling large volumes of simple requests 24/7. AI is ideal for routine tasks like order status updates, password resets, or account information.
Will AI replace human customer service agents?
No, AI will not replace human agents. AI is designed to handle simple, repetitive tasks quickly, while human agents are needed for complex or emotional issues.
The best approach is combining both: AI for speed and efficiency, and humans for empathy and problem-solving.
When should I use AI versus a human agent?
Use AI for quick, repetitive tasks like checking order status, resetting passwords, or answering common customer queries. Use a human agent for personalized support when the issue is complex, sensitive, or requires empathy and problem-solving.
What is the first step to creating a balanced AI-human support model?
The first step is mapping your customer journey. Identify which questions are simple and repetitive (best for AI) and which are complex or emotional (best for human agents).
This helps you decide where to use automation and where to keep human support.
Can AI improve customer satisfaction?
Yes. AI speeds up response times and reduces wait times, which customers appreciate. When paired with human agents for complex issues, it often leads to higher overall satisfaction.
Can AI reduce customer service costs?
Yes. By handling large volumes of simple requests, AI reduces staffing needs, cuts response times, and lowers overall support costs.



